Configuring Microsoft NAV Web Client by Modifying the Web.Config File
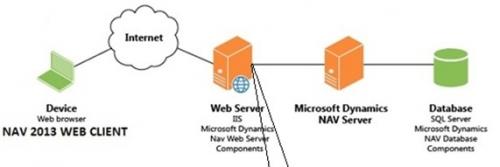
To install the Microsoft Navision Web Client, the end user has to first install the NAV 2017 Set Up. When the Set Up gets underway, a website gets installed with a web server for the NAV Web Client on an Internet Information Services (IIS) Server. The Set Up also configures the connection from the NAV Web Client to the NAV Server. Post installation, the NAV administration Shell can be used to further add additional web server instances for the NAV Web Client. Whatever connection information is there, it is all saved in the web.config file of the web server instance. Post installation, its configuration can be changed by modifying the web.config file.
What is the Web.Config File? It is an .XML File which can be edited with the help of a Text Editor such as Notepad.
How does one locate the web.config file? There are various NAV web server instances on IIS with each having its own web.config file stored in the physical path of the application’s virtual directory. The path would be %systemroot%\inetpub\wwwroot\[VirtualDirectoryName].
What are NAV Settings in the Web.Config File? After having it thoroughly customized by a Microsoft Dynamics NAV Partner, end users can find the NAV Web Client settings in <DynamicsNAVSettings>.
Companies trying to configure NAV Web Client by modifying the web.config file can request their Microsoft Dynamics Partner in India providing Microsoft Dynamics NAV Support to explain all the Settings as well as their Descriptions.
These have been written about below for better understanding:
1. AllowNtlm helps specify whether NT LAN Manager fallback in permitted for authentication or not. The value ought to be set as FALSE in case the end user needs Kerberos authentication. The default value, however, remains TRUE.
2. ClientServicesChunkSize helps set the maximum size of a chunk of data transmitted between NAV Web Client in NAV Server in kilobytes. The transmitted data is fragmented into small pieces known as chunks and subsequently reassembled at the time when it reaches its destination.
3. ClientServicesCompressionThreshold helps set the threshold in memory consumption at which the NAV Web Client begins to compress data sets. This sort of limits the amount of memory consumed, whose value is set in KiloBytes.
4. ClientServicesProtectionLevel helps specify security services used for protecting data stream between the NAV Web Client and the NAV Server. This value must match the value specified in the NAV Server Configuration File.
5. Server specifies the name of the computer running on the NAV Server.
6. ServerInstance specifies the name of the NAV Server Instance which the NAV Web Client connects to.
7. ClientServicesCredentialType helps specify the authorization mechanism used to authenticate users trying to connect with the NAV Web Client. It should be known that the credential type must match the credential type configured for the NAV Server Instance that the NAV Web Client connects to.
8. ClientServicesPort helps specify the TCP Port for the NAV Server, part of the NAV Server’s URL.
9. ServerPrincipalNameRequired is a parameter which if set as TRUE, facilitates connection of the NAV Web Client only with the NAV Server Instance associated with a service principal name. Now if the parameter is set as FALSE, the NAV Web Client attempts to connect to the configured NAV Server service irrespective of whether the service is associated with SPN or not.
10. SessionTimeout specifies the maximum time for which a connection between the NAV Web Client and NAV Server can remain idle, before the session expires. This setting determines how long an open NAV Page or Report can remain inactive before closing. The SessionTimeout usually is 20 minutes and during this time if the end user fails to take any action, the page closes and gets replaced with the message: The page has expired and the content cannot be displayed.
11. ShowPageSearch specifies whether to show the Search for Page or Report icon in the ribbon pane of the Role Center and this lets users find NAV objects, such as Pages, Reports and CodeUnits. Search for Page or Report finds only those objects that are available from the Departments page in the NAV Windows Client. In case you do not want Search for Page or Report to be available in the NAV Web Client, then you can set the parameter as FALSE.
12. DNSIdentity specifies subject name or common name of the service certificate for NAV Server and holds relevance only where the ClientServicesCredentialType is set to UserName, NAVUserPassword and AccessControlService, all of which require Security Certificates to be used on the NAV Web Client and NAV Server to protect communication.
13. ForgotPasswordLink specifies the URL which has to be opened in case the user selects ‘Forgotten Your Password?’ on the sign in the dialog box.
14. HelpServer specifies the name of the NAV Help Server that the NAV Web Client must connect to.
15. HelpServerPort specifies the TCP Port on the specified NAV Help Server that the NAV Web Client can access Help through.
So this was all about Configuring the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Web Client by Modifying the Web.Config File.
Comments