What Is Transponder and Muxponder?
Data centers and service providers face the increasing demands for data security, low latency, higher speeds and longer distances in networks. Transponders and muxponders are both key elements that receive and send the signals over the fiber in an optical transport network.
What Is Transponder?
Transponders are used to enable point-to-point connections over long distances when the client rate matches the optical wavelength. A transponder is the element that sends and receives the optical signal from a fiber in optical fiber communications. A transponder is typically characterized by its data rate and the maximum distance the signal can travel. Transponders are used to enable point-to-point connections over long distances when the client rate matches the optical wavelength. In cases where the client rates are lower than the optical wavelength, a muxponder is used to multiplex multiple sub-rate clients onto the line interface.

What Is Muxponder?
In cases where the client rates are lower than the optical wavelength, a muxponder is used to multiplex multiple sub-rate clients onto the line interface. Muxponder is used in WDM or ROADM equipment, which needs to meet the needs of any service, port Muxponder or function card on the basis of reducing power consumption and cost. Muxponder also has the capability to combine multiple services into a single wavelength by multiplexing several channels to a higher order signal.
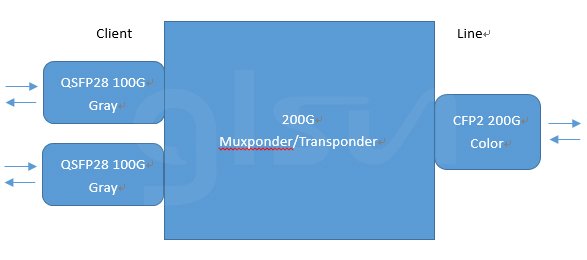
200G Muxponer supports 100G or 200G OEO card. Its main function is to convert the service signals of 1*100G-QSFP28 into 1*100G-DCO coherent transceiver or 2*100G-QSFP28 to 1*200G-DCO coherent transceiver for coherent optical transmission. The line side adopts coherent optical modulation mode, and other technologies. It supports 100GE to 100G DWDM signal (100G CFP2 DCO) conversion and 2*100GE to 200G DWDM signal (200G CFP2 DCO) conversion and realize maximum transmission without repeater of 800 km, support C-band 96 channels (50GHz).
When to Use Transponders and Muxponders?
Transponders and muxponders can automatically receive, amplify and re-transmit signals on new wavelengths without any changes to the data carried over the signal at all, which can not be achieved by only adopting transceivers. However, a solution based on active transponders or muxponders is preferable when transceivers and switches are not fully compatible or when transceivers alone could not meet the real needs.
1.When the networks need to be encrypted, transponders and muxponders can help to protect sensitive data and meet regulatory requirements with encryption.
2.When data needs to be transmitted over a long distance but the transceiver does not support long–distance WDM, an OEO-based solution with transponders and muxponders can extend the distance of WDM network and add FEC to the signal.
3.When an Internet service provider need to hand off a gray signal to end users, transponders and muxponders can help to control and restrict the bandwidth.
4.When the data needs to be transmitter at higher speeds than supported by transceivers in WDM networks, transponders and muxponders are another way to support faster speeds regardless of the transceiver form factor.
Post Your Ad Here
Comments