SQL Optimizer for SQL Server: Working in Centralized Systems

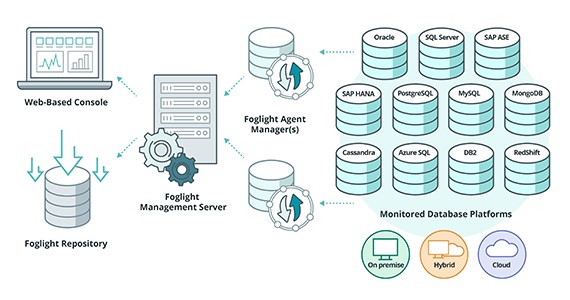
The process
of optimization in SQL might seem complex to a lot of us, especially when we
consider the operation of centralized systems. After gaining all the
alternative access paths to compute a relational algebra expression, the best
one among these is derived.
In this
post, we will explain the process of the SQL
optimizer for SQL Server to perform optimization in a centralized
system. We will also explore the various steps involved in this process.
There are
multiple reasons behind the optimization of query processing in centralized
systems. For instance, doing this will decrease the time it takes to fetch the
results for the statement and raise parallelism. It will also vastly improve
the number of requests or throughput for a given time period and decrease the
requirement for storage and memory that query processing requires.
During statement parsing and translation, the scanning of the statement takes place first, after which the parsing follows to locate syntax errors and verify data type accuracy. On completing this step, the statement breaks into smaller sections, each of which is translated into its respective relational algebra expression.

The process
of optimization by SQL Server tuning tools such as the
optimizer consists of three steps. These are query tree production, plan
creation, and statement plan code construction.
As it's name
suggests, a query tree is a data structure whose elements resemble those of a
tree. It represents a relational algebraic expression as it's leaf nodes are
the query tables whereas the root is the entirety of the query.
The inner
node goes to processing first when executing the query, in the presence of the
operand tables. The result table then falls in the node's place. Every node
finds its replacement in this manner until the root node gets processed.
Once the
query tree is created, a query plan is produced. It is essentially an elongated
query tree with space for access paths for every operation in it. An access
path is created to denote the procedure of relational operations, i.e. how they
have to be performed. For instance, the access path for a selection task might
show more information regarding the process of using B plus tree index for it.
Additionally,
a query plan also specifies the process of transferring the intermediate tables
among operators as well as the correct way to use temporary tables and
combining one or more groups of operations.
The third
and final step for the oracle query
optimizer tool involves generating the code to
complete the query optimization process. This code is the executable form of
the statement that is reliant on the type of OS underneath. After it
generation, the Execution Manager executes the code to generate the output.
There are
certain ways in which database professionals approach the database query
optimization process. These include two of the most commonly used methods:
exhaustive search and algorithms designed on heuristics.
In
exhaustive search technique, every query plan possible is fetched for a given
query. Then, we find the best and optimal query plan among these. Even though
the approach may be effective, it contains an exponential time and space
complexity because of the huge solution space.
On the other
hand, many SQL Server tuning tools use the heuristic based optimization
approach as it implements rule-based optimization. In it, the algorithms
contain far less time and space complexity as compared to exhaustive
search-based algorithms. The downside here is while this approach may take less
time and space, it may not always give the best query plan.
There are three major heuristic standards to conform to:
● Conduct
project and select tasks prior to joint ones. You can follow this rule by
pushing the two lower in the query tree. Doing this is important because it
decreases the number of tuples that will join.
● Complete
the most limiting operation (select or project) before you move to the other
operations.
● Do
not perform the cross-product operation because they always create huge intermediate
tables.

Post Your Ad Here
Comments