Everything you need to know about migraines
Migraines are severe, recurring, and debilitating headaches. They may be preceded or accompanied by sensory warning signals and other symptoms.
The intense pain that migraines trigger can last for hours or even days.
According to the American Migraine Association, they affect 36 million Americans or roughly 12 per cent of the populace.
Migraines can follow an aura of sensory disturbances followed by a severe headache which frequently appears on one side of their mind. They tend to influence people aged 15 to 55 years.
Quick facts on migraines:
• Some men and women who experience migraines may clearly identify causes or variables that cause the headaches, like allergies, mild, and stress.
• Some folks receive a warning symptom before the beginning of a migraine headache.
• Many people with migraine can stop a full-blown assault by recognizing and acting on the warning signs.
• Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs can eliminate or reduce pain, and certain medications can help some people with a migraine.
• Individuals who have severe attacks may take preventative medications.
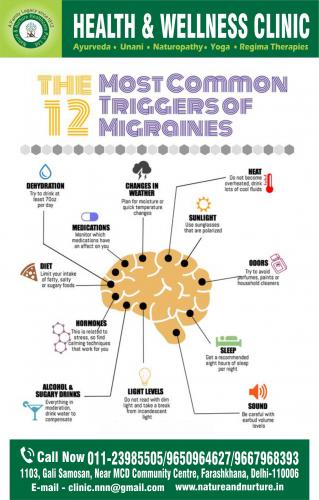
Triggers
The cause of migraines isn't yet known.
It's supposed that they result from abnormal activity in the brain. This can influence the way nerves communicate in addition to the chemicals and blood vessels in mind. Genetics can make someone more sensitive to the causes that may cause migraines.
However, the following causes are likely to put off migraines:
• Hormonal changes: Girls may experience migraine symptoms during puberty, due to changing hormone levels.
• Emotional triggers: Anxiety, melancholy, anxiety, enthusiasm, and shock can cause a migraine.
• Physical causes: Tiredness and inadequate sleep, neck or shoulder strain, poor posture, and physical overexertion have been linked to migraines. Low blood glucose and jet lag may also act as triggers.
• Triggers from the diet: Alcohol and caffeine may lead to triggering migraines. Irregular meal times and dehydration also have been named as potential causes.
• Drugs: Some sleeping pills, hormone replacement therapy (HRT) drugs, and the combined contraceptive pills have been named as potential triggers.
• Triggers from the surroundings: Flickering screens, strong scents, secondhand smoke, and loud noises may set off a migraine. Stuffy rooms, temperature changes, and bright lights can also be potential triggers.
Treatment
There's currently no single cure for migraines. Treatment is aimed at preventing a full-scale assault and relieving the symptoms that happen.
• reducing stress
Some people also discover that special diets might help, such as gluten-free.
Consider seeking additional treatment if the above changes don't alleviate the symptoms or frequency of migraines. The treatment of migraine symptoms concentrates on avoiding triggers, controlling symptoms, and taking medication.
Surgery
The past decade has witnessed the development of new approaches to treating migraines. These are a group of nerves in the neck and face linked to migraine reactions.
A 2014 review also revealed that surgical decompression of those nerves could reduce or eliminate migraines in patients who don't respond to first-line therapy.
Medications
There are lots of unique forms of insomnia medication, including painkillers.
Painkillers should be taken early in the advancement of a migraine instead of allowing the aggravation to develop.
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs useful for treating migraines include:
• naproxen
• ibuprofen
• acetaminophen
Many painkillers are available to purchase online, such as naproxen, acetaminophen, and aspirin with caffeine. Always speak to a physician before taking a new medication.
Some men and women who experience migraines will have to take drugs that treat the similar symptoms.
Metoclopramide may be used to control specific symptoms, such as nausea and vomiting. Serotonin agonists, such as sumatriptan, may also be prescribed for acute migraines or for migraines that don't respond to OTC medications.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and antidepressants, like tricyclics, are prescribed to decrease migraine symptoms, although they're not approved in most states for this purpose.
Migraine prevention starts with avoiding triggers. The principal goals of preventative therapies are to decrease the frequency, pain level, and duration of migraine headaches and increase the effectiveness of different treatments.
There are several drugs and nutritional supplements that help prevent migraine attacks, including:
• antidepressants
• coenzyme Q10
• vitamin B-12 nutritional supplements
• riboflavin
Before purchasing, ensure it is safe to take these supplements along with other drugs.
It's worth noting that some people may experience a medication overuse headache (MOH), or rebound a problem. This can happen after taking too many drugs to prevent migraine attacks.
Health and wellness clinic/ centre
Comments