Parotid Tumor: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
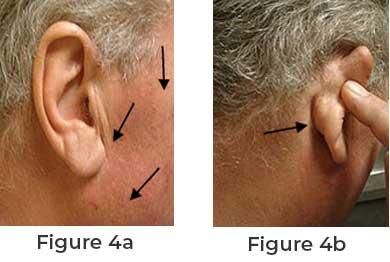
A parotid tumor is an
abnormal growth that develops in the parotid gland, the largest of the salivary
glands, located near the jaw and in front of the ears. While most parotid
tumors are benign, some can be malignant and require prompt medical attention.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of parotid tumors
is not well understood, but certain risk factors have been identified,
including:
- Radiation Exposure: Previous radiation
treatments to the head and neck region can increase the risk.
- Smoking: Tobacco use is linked to a higher
risk of salivary gland tumors.
- Genetic Factors: Family history may play a
role in the development of these tumors.
- Viral Infections: Certain viruses, such as
Epstein-Barr virus, have been associated with salivary gland tumors.
Types of Parotid Tumors
Parotid tumors can be classified
as:
- Benign Tumors: The most common type is
pleomorphic adenoma, followed by Warthin’s tumor.
- Malignant Tumors: These include
mucoepidermoid carcinoma, adenoid cystic carcinoma, and salivary duct
carcinoma, which tend to be more aggressive and require extensive
treatment.
Symptoms of Parotid Tumors
Parotid tumors may present with
various symptoms, such as:
- A painless lump or swelling near the jaw or
ear.
- Facial weakness or paralysis, which may
indicate a malignant growth.
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking.
- Pain or discomfort, especially in malignant
cases.
- Numbness or tingling in the face.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a parotid tumor
involves:
- Physical Examination: A doctor will check
for swelling or masses in the parotid gland area.
- Imaging Tests: MRI, CT scans, or ultrasound
can provide detailed images of the tumor.
- Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB): A
sample of the tumor cells is extracted to determine whether it is benign
or malignant.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the type and
stage of the tumor:
- Surgical Removal: Most benign and malignant
tumors require surgical excision, often via parotidectomy.
- Radiation Therapy: Used in malignant tumors,
especially if complete surgical removal is not possible.
- Chemotherapy: Typically reserved for
aggressive or advanced malignant tumors.
- Rehabilitation: If facial nerve damage
occurs, physical therapy or reconstructive surgery may be needed.
Conclusion
Parotid tumors are often benign but require careful evaluation and treatment to prevent complications. Early diagnosis and intervention improve the prognosis, particularly for malignant cases. If you notice any persistent swelling or facial changes, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Post Your Ad Here

Comments