The Significance of Heritage Management in Preserving Cultural Heritage
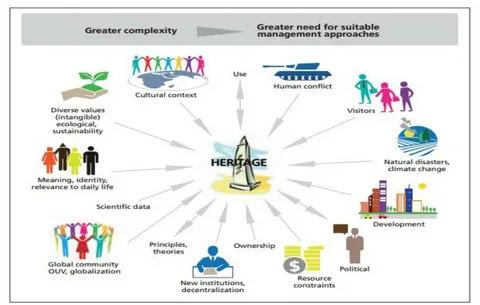
Heritage management is an essential practice that aims to identify, protect, and promote cultural heritage assets. As societies progress and evolve, the importance of safeguarding our historical, cultural, and environmental legacies becomes increasingly evident. This article will delve into the key aspects of heritage management, the challenges faced, the role of various stakeholders, and how effective management contributes to community sustainability. The internal linking keyword heritage management services will also be incorporated for better navigation within your content.
What is Heritage Management?
Heritage management encompasses a broad spectrum of practices designed to protect and manage cultural heritage assets. This includes both tangible heritage, such as historic buildings, monuments, and artifacts, and intangible heritage, including traditions, languages, and customs. Heritage management ensures that these assets are preserved for future generations, allowing them to learn from and appreciate their cultural roots.
The significance of heritage management extends beyond mere preservation; it plays a crucial role in fostering community identity and pride. It helps local populations connect with their history and understand the narratives that have shaped their present. This connection can enhance community cohesion and promote a sense of belonging.
Key Principles of Heritage Management
Effective heritage management is guided by several key principles:
Identification and Documentation: The first step in heritage management is identifying and documenting cultural assets. This involves conducting surveys, historical research, and assessments to create an inventory of heritage sites and elements. Accurate documentation is crucial for understanding the significance and context of these assets.
Conservation and Preservation: Once cultural assets are identified, conservation efforts must be implemented. This can involve physical restoration of historic buildings, maintenance of archaeological sites, and safeguarding of intangible cultural practices. Preservation aims to maintain the integrity of heritage assets while ensuring they remain relevant to contemporary society.
Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in heritage management is essential. Community involvement not only fosters a sense of ownership but also brings diverse perspectives into the management process. Local knowledge can enhance conservation efforts and promote sustainable practices that align with community values.
Sustainability: Heritage management must consider the long-term sustainability of cultural assets. This involves balancing preservation with economic development, ensuring that heritage sites are accessible and relevant. Sustainable practices can include adaptive reuse of historic buildings for modern purposes, thus preserving their significance while serving contemporary needs.
Education and Awareness: Raising public awareness about the importance of cultural heritage is vital for its preservation. Educational programs and outreach initiatives can inform the public about the significance of heritage assets and encourage active participation in their protection. Schools, museums, and community organizations can play a crucial role in promoting heritage education.
The Role of Heritage Management Services
Heritage management services are provided by various organizations, including governmental bodies, non-profit organizations, and private firms. These services typically involve consultation, project management, and technical assistance in developing preservation plans. Engaging heritage management services can greatly enhance the effectiveness of heritage preservation efforts.
For instance, professional heritage managers may conduct assessments to determine the condition of heritage sites, provide guidance on conservation techniques, and facilitate community engagement initiatives. They can also assist in navigating the legal and regulatory frameworks that govern heritage management, ensuring compliance with relevant laws and guidelines.
Challenges in Heritage Management
Despite its importance, heritage management faces several challenges:
Urban Development: Rapid urbanization poses a significant threat to cultural heritage. As cities expand, historic sites may be demolished or altered to make way for new developments. This often leads to conflicts between development interests and heritage preservation. Effective heritage management requires finding a balance between accommodating growth and safeguarding cultural assets.
Climate Change: Climate change presents a formidable challenge to heritage management. Rising sea levels, increased frequency of extreme weather events, and changing environmental conditions can jeopardize the integrity of cultural heritage sites. Heritage managers must develop adaptive strategies to mitigate these risks, including strengthening infrastructure and implementing sustainable practices.
Funding Constraints: Limited financial resources can hinder heritage preservation efforts. Many heritage management initiatives rely on government funding or grants, which can be inconsistent. Exploring alternative funding sources, such as public-private partnerships and community fundraising efforts, is crucial for sustaining heritage management projects.
Lack of Awareness: A lack of awareness and understanding of the value of cultural heritage can impede preservation efforts. Engaging communities and raising public awareness about the significance of heritage assets is vital for garnering support for preservation initiatives.
Best Practices in Heritage Management
To overcome these challenges, several best practices can be employed in heritage management:
Collaborative Approaches: Involving a diverse range of stakeholders, including local communities, government agencies, and non-profit organizations, fosters a collaborative approach to heritage management. This ensures that various perspectives and expertise contribute to the decision-making process.
Capacity Building: Investing in capacity-building initiatives can enhance the skills and knowledge of heritage managers and community members. Workshops, training programs, and internships can empower individuals to actively participate in heritage preservation efforts.
Sustainable Practices: Implementing sustainable practices in heritage management can help protect cultural assets while addressing modern needs. This can involve integrating renewable energy solutions in heritage sites, promoting eco-friendly tourism, and advocating for sustainable urban planning.
Monitoring and Evaluation: Regular monitoring and evaluation of heritage management initiatives are essential for assessing their effectiveness. This can involve setting clear objectives, measuring progress, and making adjustments as needed to ensure successful outcomes.
Conclusion
Heritage management is a vital practice that ensures the preservation of cultural assets for future generations. By recognizing the significance of our heritage and implementing effective management strategies, we can foster community identity, promote sustainability, and protect our shared history. Engaging with heritage management services can provide valuable expertise and resources, enhancing the effectiveness of preservation efforts.
In a rapidly changing world, the need for heritage management has never been more crucial. By prioritizing the protection of our cultural heritage, we not only safeguard our past but also enrich our present and future. Communities that embrace their heritage create a strong foundation for resilience, identity, and growth.
This article incorporates the keyword heritage management services for internal linking purposes, providing a seamless connection to related content on your website.









Comments