What is plastic injection molding? A beginner’s guide
Plastic injection molding has revolutionized manufacturing across countless industries. As its popularity continues to grow into 2024, many people still find themselves asking: what is plastic injection molding exactly and why does it matter? As a professional plastic injection molding manufacturer, I will help you find it out!
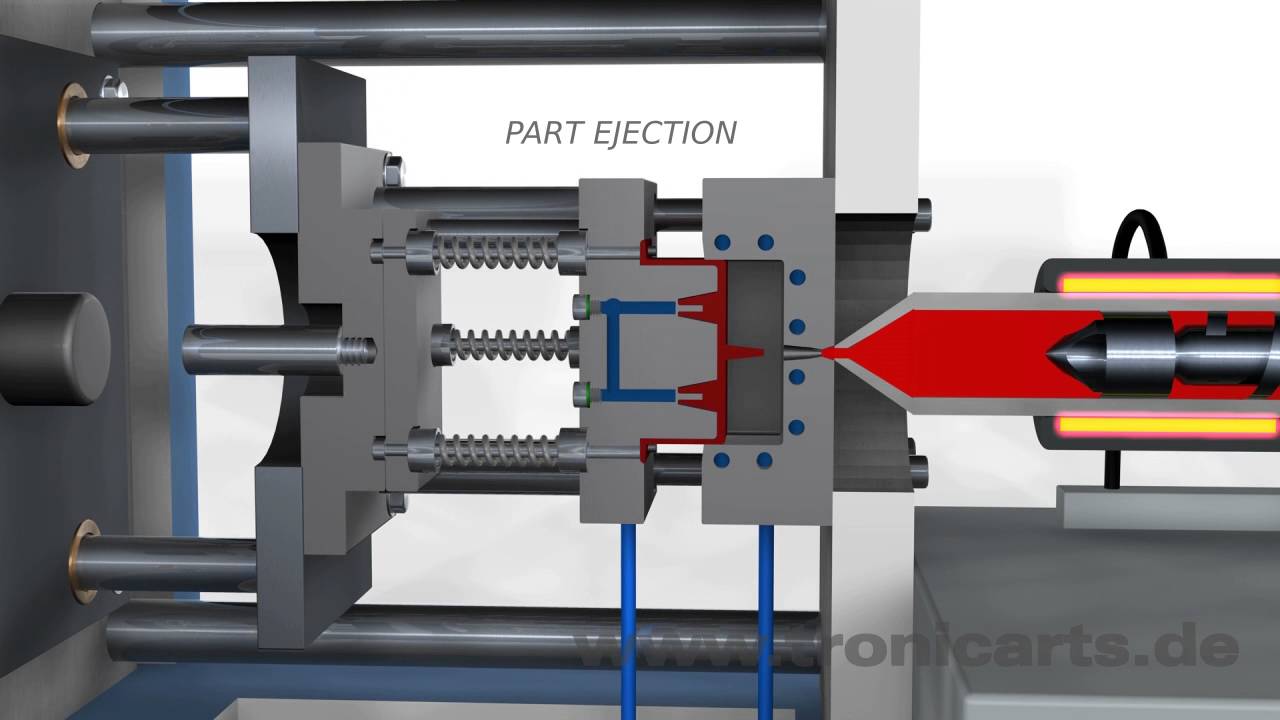
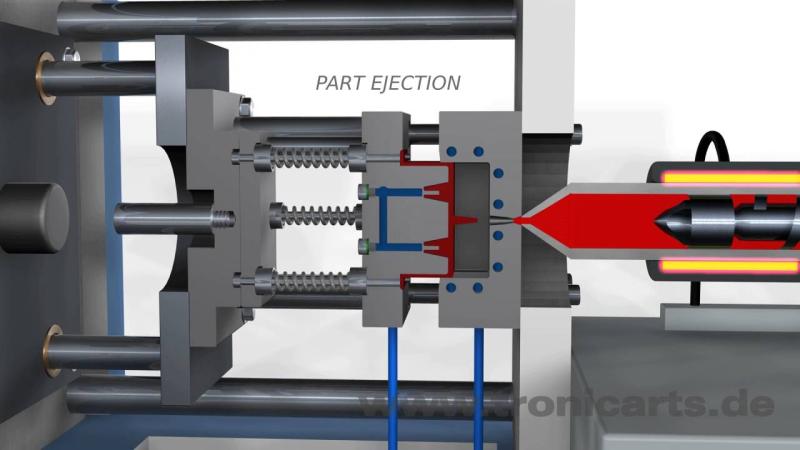
What is plastic injection molding?
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing plastic parts in large volumes. It works by injecting molten plastic material into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies into the final part shape.
The first step starts with plastic pellets, which are fed into a huge reciprocating screw housed inside the injection molding machine. As the screw turns, it melts the plastic using heaters and shear stress. Once molten, the plastic gets injected under high pressure into the mold cavity, where it packs against the cold walls of the mold and solidifies. After sufficient cooling time, the mold opens and the finished plastic part gets ejected.
This cycle then repeats to mass produce identical plastic components at a low cost per part. Injection molding enables complex geometries with tight tolerances to be shaped from various plastic materials for almost limitless applications.
Why plastic injection molding matters
Plastic injection molding offers unique manufacturing advantages that have made it indispensable for fabricating the plastic parts we use every day:
1. Highly efficient mass production
Injection molding produces complex and intricate plastic parts efficiently and accurately in large volumes, making it ideal for mass production scenarios. The process is highly automated using machines, enabling entire production cycles to be completed rapidly and reliably around the clock.
Hence, injection molding delivers unparalleled productivity and throughput using a continuous production workflow. The high initial costs of mold tooling get offset subsequently by the low per-unit costs of parts produced. Ultimately, this makes injection-molded plastic components extremely cost-effective.
2. Material versatility
Injection molding can shape plastics that offer distinct material strengths. By selecting suitable plastics, components can gain properties like strength, flexibility, heat or chemical resistance according to application requirements.
Common thermoplastics used include:
- Polypropylene (PP) – Fatigue and chemical resistance
- Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) – Strength and heat resistance
- Polyamide (nylon) – Extreme durability and low friction
- Polycarbonate (PC) – Optical clarity and impact resistance
Such versatile material options let designers fully customize parts for specialized applications and extreme operating conditions.
3. Complex geometries and precision
Unlike manufacturing processes that subtract material, injection molding can form complex and intricate plastic parts using mold cavities. This enables elaborate shapes with fine details to be produced, eliminating the need for assembly across multiple components.
Parts with diverse surface finishes, textures, and decorative patterns can likewise be fabricated directly. Mold cooling channel designs also promote uniform solidification to prevent defects. Consequently, injection molding consistently yields high precision plastic components within tight dimensional tolerances.
Applications of plastic injection molding
Thanks to its unique advantages, plastic injection molding now propels manufacturing across diverse industries:
Automotive industry
From trim components and housings to entire car body panels and bumpers, automotive manufacturing relies on plastic injection molding to produce lightweight and durable components efficiently. Special engineering plastics can endure harsh under-hood conditions over extended product lifecycles.
Medical industry
Precision plastic components enable modern medical equipment and devices for healthcare applications. Tight tolerances ensure accurate fit, assembly, and performance, while specialized medical grades offer biocompatibility. Diagnostic kits utilize custom injection molded consumables and disposables as well.
Electronics industry
Durable plastic enclosures and chassis protect delicate PCB assemblies in consumer appliances, communications devices, computing equipment, and industrial electronics. Elaborate exterior plastic casings formed via insert molding also provide functional features alongside sleek aesthetics.
Consumer goods
Plastic injection molding allows endless variety in shapes, textures, and colors for consumer products. Toys, kitchenware, containers, furniture, and many everyday plastic items now extensively leverage these molding capabilities. Both prototyping and mass production needs can be addressed.
In essence, injection molding has immensely broadened design possibilities with plastics across nearly every manufacturing sector imaginable today. It has single-handedly enable smaller, integrated, customizable, and specialized plastic parts to be produced at scale economically. Our modern manufactured world would look very different without it!
Conclusion
Fundamentally, what is plastic injection molding about? It is an indispensable manufacturing process that forms versatile plastic components for diverse mass production applications via mold cavities. Efficient, automated, and precise, injection molding offers unrivaled productivity in shaping elaborate and customizable geometries. The wide selection of plastic materials available also imparts specialized mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties to meet challenging manufacturing requirements.
In a nutshell, plastic injection molding delivers value across manufacturing sectors through its efficiency, consistency, precision, and flexibility. It’s why injection-molded plastic parts have become integral in almost everything surrounding us!




Comments