What does ESG stand for environmental social?
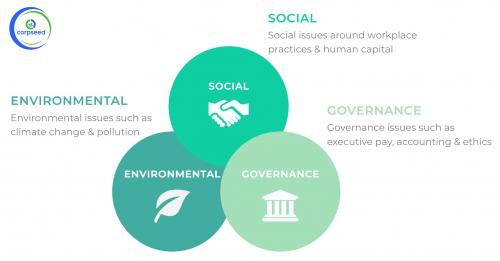
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. It is a set of standards used to evaluate the sustainability and societal impact of companies and organizations. Environmental factors include a company's impact on the environment, such as its carbon footprint and environmental policies.
Social factors include a company's treatment of its employees and its impact on society, such as its diversity and inclusion policies and labor practices. Governance factors include a company's leadership and management, as well as its financial reporting and transparency. ESG is used by investors as a way to evaluate the long-term ESG sustainability of a company and its potential risks and opportunities.
Five ways that ESG creates value
- Risk Management: Adopting ESG practices can help companies identify and mitigate potential risks, such as environmental hazards and labor disputes, which can lead to financial losses.
- Cost Savings: Implementing sustainable practices can lead to cost savings, such as reducing energy and water consumption, which can result in lower operating costs.
- Increased Efficiency: Companies focusing on ESG can improve their operations and processes, leading to increased efficiency and productivity.
- Reputation and Branding: Companies with strong ESG practices are often viewed positively by consumers and stakeholders, which can lead to improved reputation and branding.
- Access to Capital: Companies with strong ESG practices may have better access to capital, as investors are increasingly looking for sustainable investments that align with their values. Additionally, companies with strong ESG practices may be able to attract and retain top talent, which can also create value.
Environmental social and governance (ESG) investing
ESG investing is an investment strategy that focuses on companies that have strong environmental, social, and governance practices. Investing involves analyzing a company's performance in areas such as climate change, labor rights, and corporate governance, and then using this information to make investment decisions. The goal of ESG investing is to achieve financial returns while also promoting positive social and environmental outcomes.
ESG data is used to evaluate companies and their performance across three dimensions: environmental, social, and governance. Environment ESG analysis examines a company's environmental impact, policies, and management systems. Social analysis focuses on a company's impact on society, including labor practices, human rights, and community engagement. Governance analysis looks at a company's leadership, management, and transparency.
ESG investing has been gaining popularity in recent years, as investors are becoming more aware of the social and environmental impact of their investments. Additionally, some investors believe that companies with strong ESG practices are more likely to be sustainable and have better long-term performance.
However, it's important to note that different methodologies and data sources are used to evaluate companies' performance and some of the ESG metrics may not be standardized, which can make it difficult to compare companies and funds. Furthermore, some critics argue that it's difficult to assess the true impact of a company's ESG practices, as well as the correlation between a company's ESG performance and its financial performance.
Environment, Social and Governance (ESG) Strategies
Environment, Social, and Governance (ESG) strategies refer to investment approaches that take into account environmental, social, and governance factors in the selection and management of investments.
There are several different types of ESG strategies, including:
- Negative screening: This approach involves excluding companies that have poor environmental or social practices, such as those involved in tobacco or weapons production, from investment portfolios.
- Positive screening: This approach involves actively seeking out companies that have strong environmental and social practices, such as those involved in renewable energy or sustainable agriculture.
- Impact investing: This approach involves investing in companies or projects that have a specific environmental or social impact, such as investing in renewable energy projects to combat climate change.
- Best-in-class: This approach involves selecting the companies within a specific industry that have the best ESG practices, and weighting them more heavily in the portfolio.
- Thematic Investing: This approach involves investing in companies that are exposed to specific ESG themes such as clean energy, water scarcity, sustainable agriculture, among others.
- Shareholder engagement and proxy voting: This approach involves engaging with companies to encourage better ESG practices, and voting on shareholder proposals related to ESG issues.
ESG strategies can vary widely in their focus and intensity. Investors may choose to adopt a more passive approach, such as excluding companies with poor ESG practices, or a more active approach, such as actively seeking out companies with strong ESG governance practices. It's worth noting that the best approach depends on the individual's personal values and investment goals.
Read more This blog:- ESG Reporting: How dose it Differ from sustainability Reporting



Comments