Types of Financial Statements: A beginners’ Guide
Types of financial statements:
Financial Statements are the financial documents providing significant information about the financial activities of the business entity. These statements provide relevant financial data for internal and external users of accounting. The information in financial statements is useful for users of accounting in making economic decisions. There are five types of financial statements that we will learn in this article.
The types of financial statements based on US GAAP and IAS 1 issued by IASB are as follows.
- Statement of financial position
- Income Statement
- Statement of changes in equity
- Statement of cash flows
- Notes to financial statements (Disclosure)
Types of financial statements
1) Statement of financial position
The Statement of financial position is a structured presentation of the assets, liabilities, and equity of the business on a particular date.
It is a detailed representation of a fundamental equation which means all the resources (assets) owned by the entity are financed through the sources of either debt or equity.
A statement of financial position (formerly called a balance sheet) is also referred to as a statement of net worth.
Key Points
- The statement of financial position shows the financial picture of the business on a particular date (i.e., as of June 30, 2020, or December 10, 2020.).
- It has three major components: Assets, liabilities, and equity (capital).
- We can divide it into two parts: The upper half of the statement shows the assets of the entity and the lower half of the statement shows owners’ equity and liabilities.
- As the name of the balance sheet suggests, Assets = liabilities + shareholders’ equity.
- The statement of financial position is not a statement of value. It would require further analysis to arrive at a valuation.
2) Income Statement
The income statement is a financial document providing detailed information about revenues, expenses, and profit or loss for a specific period.
It helps users of the income statement to assess and measure the financial performance of an entity. We also know it as a statement of profit or loss.
Key Points
- The main objective of the income statement is to assess the profitability and financial performance of the entity.
- It also helps to predict the future performance of the entity.
- Accountants prepare it for a specific period (i.e., for the month, for the year)
- There are three major components of the income statement: revenues, expenses, and profit or loss.
- The income statement has two forms, multi-step and single step.
- Small-scale entities report the Income statement on a cash or accrual basis. However, Large-scale entities use the accrual basis, a recommended method by the FASB.
3) Statement of Cash Flows
A statement of cash flows provides information about where a business obtained its cash, and how that cash was used during the financial period.
As per IAS 1, the statement of cash flows is a part of a complete set of the financial statements of an entity.
IAS 7 requires entities to report cash flows for the period under three sections:
- Operating activities
- Investing activities
- Financing activities.
The statement of cash flows is extremely valuable because it helps in the reconciliation of the beginning and ending cash on the balance sheet.
Key Points
- It shows the movement of cash and cash equivalents.
- We prepare it for a specific period, just like an income statement (i.e., for the month, for the year).
- IAS 7 specifies the content and format of the statement of cash flows.
- The total of the cash flows for all three sections together explains the overall increase or decrease in cash and cash equivalents during the period.
- There are two approaches to identify cash flows from operating activities: The indirect method, and the Direct Method.
Read more about the cash flow statement
4) Statement of changes in equity
Changes in equity is the increase or decrease in the net assets of the entity. The statement of changes in equity tells users about the status of the owners’ equity at the beginning of the financial year, how it changed during the year, and the status of the equity at the end of the year.
It helps users to identify the key factors responsible for changes in owners’ equity over the accounting period.
It is helpful for shareholders because it provides great insights into the effects of business operations over their investment in a business.
Key Points
- It shows the status of overall changes in owners’ equity.
- The components of a statement of changes in equity are: Share capital, share premium, dividend, bonus shares, right shares, and retained earnings.
- It is helpful for users of financial statements, particularly shareholders.
Let’s understand the major differences among types of financial statements through the following Image.
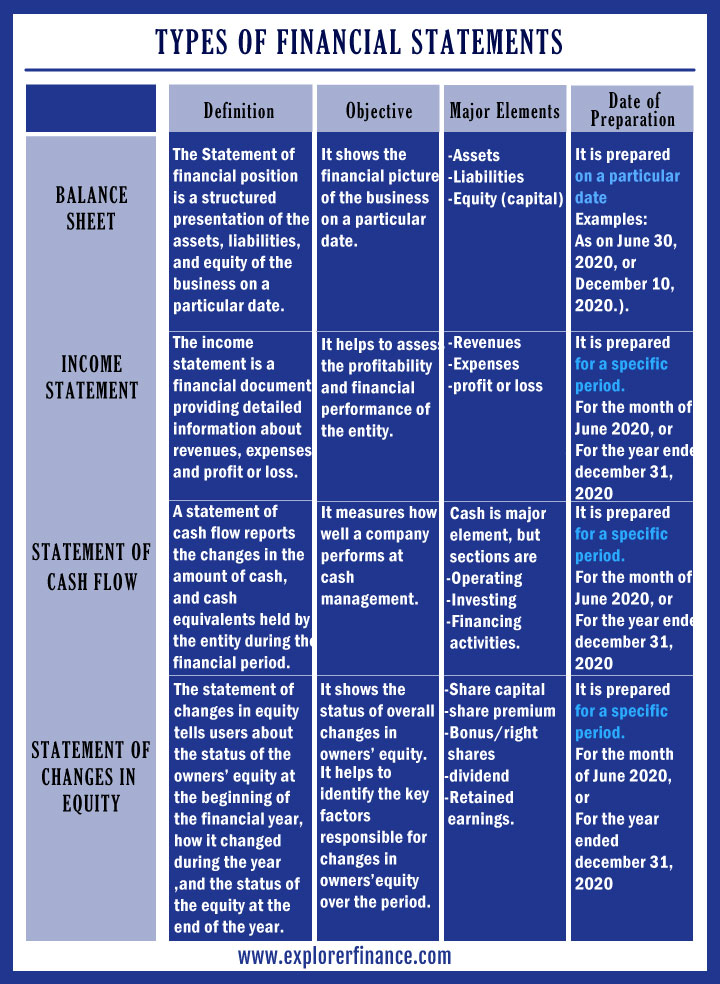
5) Notes to Financial Statements (Disclosure)
Notes are additional information together with the other four types of financial statements. It requires an entity to disclose all information that matters and help users to have a better understanding because this is the mandatory requirement by IFRS.
It provides additional information that is not presented on the face of the financial statements but is relevant to an understanding of them.
A specific order for the presentation of notes is:
- a statement of compliance with IFRS
- a summary of significant accounting policies applied
- supporting information for items presented in financial statements
- Other disclosures
Post Your Ad Here
Comments