Symptoms of Mucoepidermoid Cancer and Its Treatment
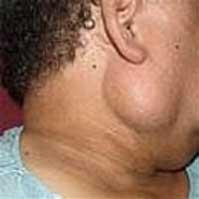
Mucoepidermoid cancer is a form of cancer commonly occurs in the salivary glands. Although it can also affect other areas such as the lungs, skin and other parts of the body. Mucoepidermoid cancer is generally slow-growing and often asymptomatic in the early stages. However, as the tumor grows, various symptoms may manifest, indicating the need for medical attention.
The symptoms of mucoepidermoid cancer can vary depending on the affected area, but commonly include:
· Swelling or lump - A noticeable lump or swelling in the affected gland or organ.
· Pain - Discomfort, tenderness, or pain in the affected area that may persist or worsen.
· Difficulty swallowing - When the cancer occurs in the salivary glands, it may lead to trouble swallowing or speaking.
· Numbness or weakness - In the facial muscles or affected region, leading to issues with movement or sensation.
· Changes in skin - Skin changes like redness, ulceration, or discoloration in the affected area.
· Persistent cough or breathing difficulties - When the tumor affects the lungs, it might lead to a chronic cough, wheezing, or shortness of breath.
Early diagnosis is crucial in managing mucoepidermoid carcinoma. If you notice any of these symptoms, it's vital to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and potential treatment. Regular check-ups and prompt medical attention can greatly impact the prognosis and management of this condition.
Know About the Treatment Procedure for Mucoepidermoid Cancer
The treatment for mucoepidermoid carcinoma depends on several factors, including the tumor's size, location, and grade, as well as the patient's overall health. Typically, treatment options include surgery, radiation therapy, and sometimes chemotherapy.
Surgery is often the primary treatment, aiming to remove the tumor and any affected tissue. In cases where the tumor is small and localized, surgery might be the sole treatment needed. However, if the cancer has spread to surrounding tissues or lymph nodes, additional treatments such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy may be necessary to ensure any remaining cancer cells are eliminated.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to target and destroy cancer cells, often employed post-surgery to eradicate any remaining cancer cells. Chemotherapy, although less common, might be considered in certain cases to help control the disease's progression or to address metastatic MEC.
In recent years, advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapies have shown promise in treating various types of cancer, including mucoepidermoid carcinoma. These treatments aim to better target cancer cells, minimizing damage to healthy tissues and reducing side effects.
Keep Some Key Points in Mind
It's important to note that the approach to treatment will vary based on individual circumstances, and patients should consult with a medical team specialized in oncology to determine the most suitable and effective treatment plan tailored to their condition. Regular follow-ups and monitoring are crucial for tracking the effectiveness of treatment and managing any potential side effects or recurrences.

Comments