Steel Recycling: Reusing Strength for a Sustainable Future
Steel,
the backbone of modern civilization, is an essential material used in
construction, infrastructure, vehicles, appliances, and countless other
applications. But producing steel from scratch requires vast amounts of energy
and iron ore, a finite resource. This is where steel scrap comes in, offering a
sustainable and cost-effective alternative.
Steelmaking
is an energy-intensive process. Extracting iron ore, the primary raw material for virgin steel, uses
significant amounts of energy and disrupts natural habitats. Refining the ore into usable iron further
increases the environmental impact. Steel scrap, on the other hand, provides a ready-made source of steel
without the need for extensive extraction and refining processes. This translates to a significant reduction in
energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, making steel recycling a
critical element of sustainable steel production thus impact the scrap steel
price in India and global.
The Power of Recycling: Steel Scrap in Steelmaking
Steel
scrap is any discarded steel item that can be reprocessed into new steel
products. It comes from various sources like:
End-of-Life Products: Cars, appliances, machinery, and buildings generate a significant
portion of steel scrap.
Industrial Byproducts: Steel mills themselves produce scrap during the
manufacturing process.
Manufacturing Trim: Excess steel pieces cut from sheets or during fabrication
become valuable scrap.
Steel
scrap plays a crucial role in modern steelmaking, offering several advantages:
Reduced Energy Consumption: Remelting scrap steel requires significantly less
energy compared to virgin iron ore. This translates to lower greenhouse gas
emissions and a smaller environmental footprint.
Cost-Effectiveness: Scrap is generally cheaper than virgin iron ore, leading to
lower production costs for steel mills.
Improved Quality: Modern electric arc furnaces (EAFs) effectively utilize
scrap to produce high-quality steel with desired properties.
Resource Conservation: Recycling steel scrap reduces reliance on depleting iron ore
reserves and minimizes landfilling.
Scrap Rate Today: Understanding the Numbers
The
global steel scrap usage rate, also known as the scrap rate, is a critical
metric indicating the industry's dependence on recycled steel. The scrap rate
today is depending on demand and supply from industries and the demand of
secondary steel is rising.
For instance, according to Fact.MR, the global steel scrap market was valued at 655 million metric tons in 2023 and is projected to reach 1,050 million metric tons by 2033, reflecting a steady growth at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 4.9%.
Steel Scrap Rate in India
India,
a major steel producer, is also witnessing a rise in scrap utilization. a
report by the Steel Recycling Institute (SRI) of India suggests the country's
crude steel production mix reached 23% scrap usage in 2021-22. This indicates a
growing trend towards sustainable steelmaking practices.
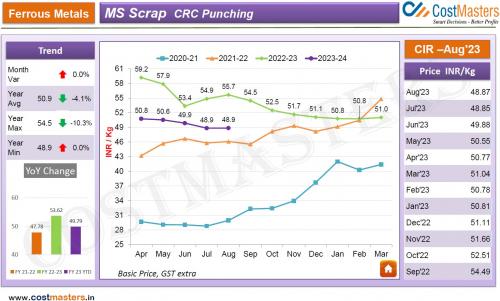
steel
scrap rate in India is depended on the type of scrap and demand. For instance,
the according to CostMasters’s Cost Intelligent Report published in February’24
the MS scrap cost is show’s a decreased of 17.3%.
Steel
Scrap Rate in India decreased due to less demand and falling price of
primary steel.
Beyond Steelmaking: Diverse Uses of Steel Scrap
While
steelmaking remains the primary application, steel scrap finds uses in several
other industries
Construction: Crushed scrap is used as aggregate in concrete mixes and for
road construction.
Foundries: Steel scrap serves as a cost-effective raw material for casting various
metal products.
Agriculture: Shredded scrap is used for soil stabilization and erosion
control.
Shipbuilding: Dismantled steel ships are often recycled to create new
vessels.
Price Trends: Navigating the Steel Scrap Market
The
price of steel scrap fluctuates based on several factors, including:
Supply and Demand: A surge in demand or a limited supply can push prices
upwards. Conversely, an oversupply can lead to lower prices.
Scrap Type and Quality: High-grade steel scrap with minimal impurities generally
commands a premium price.
Global Market Conditions: Economic factors and international trade policies can
influence scrap prices.
While
real-time price data is industry-specific, various resources track historical
trends and offer market forecasts. Staying informed about these trends helps
businesses optimize their scrap management strategies.
The Future of Steel Scrap: Embracing Sustainability
The
steel industry is increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainability.
Steel scrap is a vital component in achieving this goal. As technology advances
and global steel demand grows, the role of scrap is expected to become even
more prominent:
Innovation in Scrap Processing: New technologies for sorting,
processing, and cleaning scrap will enhance its usability and value.
Focus on Circular Economy: The industry will strive to create a closed-loop
system where steel products are designed for easier recycling after their
lifespan.
Government Regulations: Policymakers are likely to implement regulations encouraging scrap utilization and responsible waste management.
Post Your Ad Here
Comments