How To Chart An IoT Road Map?
 What are the essential elements for designing an IoT strategy? What kind of capabilities do you need? What are the roadblocks and how can you overcome them?
What are the essential elements for designing an IoT strategy? What kind of capabilities do you need? What are the roadblocks and how can you overcome them?One of the main reasons why the popularity of Internet of Things (IoT) is increasing by leaps and bounds is it is disruptive as well as transformative in nature. Disruptive because it radically challenges the manner in which how most businesses work, and transformative because it introduces new technology platforms in organizational work processes. According to Gartner Inc., it is estimated that approximately 8.4 billion devices will be connected through IoT by the end of 2017, while McKinsey Global Institute, yet another private-sector “think tank” company analyzing the evolution of the global economy estimates that IoT market shall grow between $3.9 trillion to $11.1 trillion by 2025.
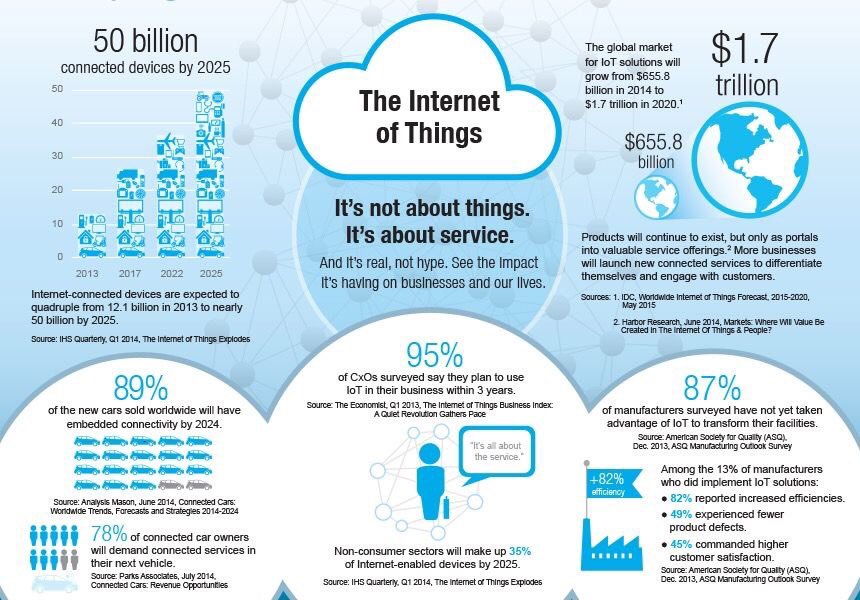
While industrial verticals such as manufacturing, transport and logistics, and supply chain industries have realized the importance of using IoT technology to reduce operational overheads and increase profits, other verticals like public services, healthcare, retail, consumer products, etc. are expected to follow suit in the long run.
Five essential elements for designing an IoT strategy
1. An IoT strategy should focus upon some business value that can significantly impact the organization in a positive manner, such as an increase in revenue or growth, or an improvement in the work processes that can drastically increase productivity levels of employees or improve their work efficiency levels to yield better profits for the company.
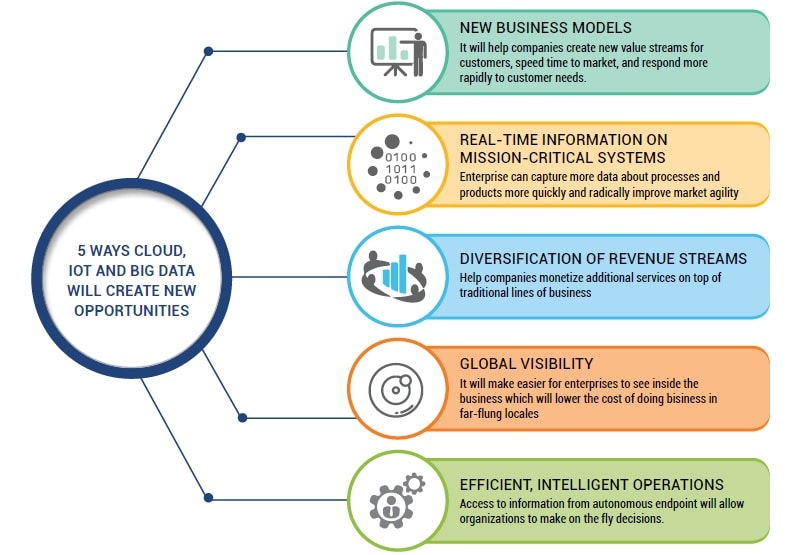
2. The second element should focus on consistency in thoughts and use a top-down approach to identify problematic issues or non-productive assets currently employed by the organization. The management should not lose its focus as to what it proposes to achieve using IoT and what it can gain through its implementation.
3. The third element suggests a well-defined ecosystem that can meet the scope of all IoT related processes and systems. Internet of Things technology depends heavily upon supportive hardware and devices which can further add on to the project budget. Technology acquisition, technical training and the cost of devices incur certain costs and managements have to plan the budget accordingly to sustain the ecosystem over time.
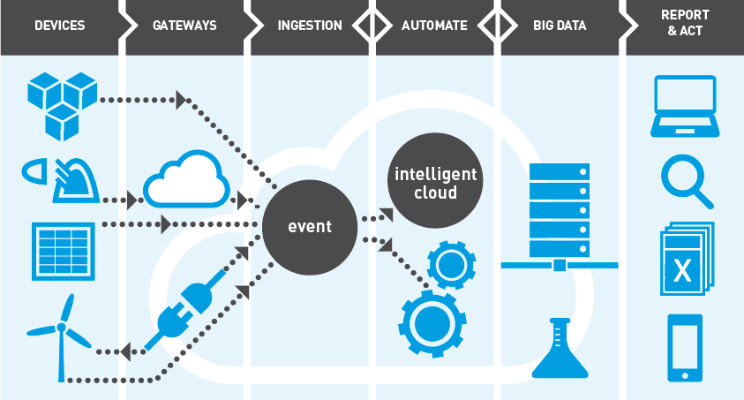
The second issue is that disruptive technologies constantly evolve and organizations are required to invest in time, efforts and money to keep pace with technological advancements.
4. The fourth element concerns skill sets and capability levels of the organization’s tech team. Does the team include engineers and technicians who’re well versed with proposed IoT technologies? Do they require additional training? Can they be trained? Do you need to recruit new tech personnel? Can you outsource technology maintenance aspects?
5. The fifth element takes into consideration how change management affects an organization’s workforce and the willingness of people in embracing IoT.
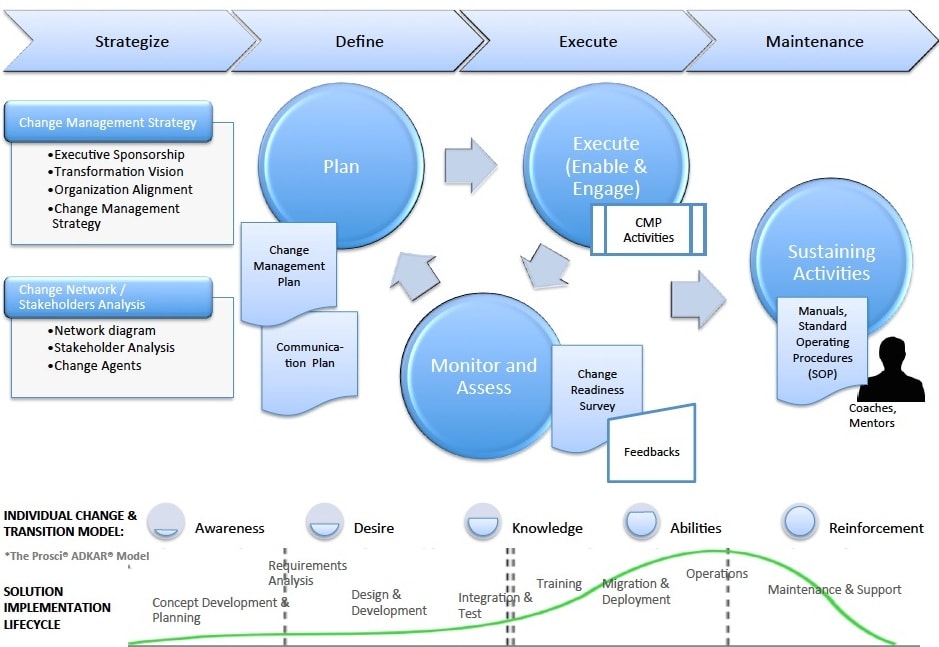
A concept that radically challenges how people work and proposes new ways of working doesn’t always go well with the teams. Organizations have to work out proper plans to support change management.
Five capabilities for executing the strategy
Skills
Organizations have to depend heavily on the skill sets of their tech teams to design and develop their business processes. IoT requires an understanding of technical aspect pertaining to embedded systems, networking knowledge, computer programming, machine learning, big data, network security, UI / UX design, mobile development, etc.
Change management
As explained before, people may find it difficult to accept new ways of working, and may even resent adopting new processes and methods. It is important that teams open up... Read more.






Comments