What Are Tokens and How Do They Work?
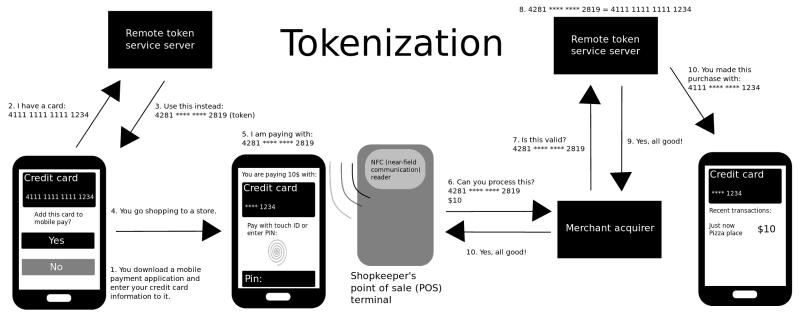
In the digital age, the term "token" has gained significant prominence, particularly in the realms of blockchain, cryptocurrencies, and online security. But what exactly are tokens, and how do they function in different contexts? This article delves into the concept of tokens, their types, and their operational mechanisms.
Understanding Tokens
A token is a digital representation of value, utility,
or ownership. It is not limited to a single application but varies depending on
its purpose and platform. Tokens are most commonly associated with blockchain
technology, where they play a crucial role in decentralized ecosystems. However,
they are also used in broader applications like authentication systems, digital
access, and gaming environments.
Types of Tokens
Tokens can be broadly classified into the following
categories:
- Cryptocurrency Tokens:
Cryptocurrency tokens, often simply called "cryptos," represent
a digital currency that operates on a blockchain. Bitcoin (BTC) and
Ethereum (ETH) are classic examples. These tokens serve as a medium of
exchange, store of value, and unit of account in digital transactions.
- Utility Tokens: Utility tokens provide access to a product or
service within a specific blockchain ecosystem. They are not intended as
investments but as tools to utilize a particular platform. For example,
Basic Attention Token (BAT) is used in the Brave browser ecosystem to reward
users for their attention.
- Security Tokens: Security tokens represent ownership in an
asset, such as shares in a company, real estate, or other investment
instruments. They are regulated financial products, similar to traditional
securities but operate digitally on a blockchain. An example is tZERO, a
security token trading platform.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): NFTs are unique digital assets
that represent ownership of a specific item, such as digital art, music,
or collectibles. Unlike other tokens, NFTs are not interchangeable due to
their uniqueness. They operate on blockchain standards like Ethereum’s
ERC-721.
- Governance Tokens: These tokens
provide holders with voting rights in decentralized protocols. For
example, UNI tokens allow users to participate in governance decisions
within the Uniswap ecosystem.
How Tokens Work
Tokens typically operate on blockchain networks. A
blockchain is a decentralized ledger that records all transactions and ensures
transparency and security. Here’s a closer look at the operational mechanism:
- Creation: Tokens are created using
smart contracts, which are self-executing programs with predefined rules.
Platforms like Ethereum make token creation accessible through standards
such as ERC-20 (for fungible tokens) and ERC-721 (for NFTs).
- Storage: Tokens are stored in digital wallets, which are
software or hardware solutions that interact with blockchain networks.
Each wallet has a unique address, allowing users to send, receive, and
manage their tokens securely.
- Transactions: Transactions involving tokens are recorded on
the blockchain. Once a transaction is initiated, miners or validators
verify it, ensuring it adheres to the network’s consensus rules. Once
validated, the transaction is added to a block and becomes immutable.
- Utility: Depending on their type, tokens serve various
purposes. For instance, cryptocurrency tokens facilitate payments, while
utility tokens provide access to services. Security tokens represent
ownership, and NFTs certify authenticity and ownership of unique assets.
- Transferability: Tokens can be
transferred between users without intermediaries, thanks to the
decentralized nature of blockchain networks. This makes them highly
versatile for global use.
Advantages of Tokens
Tokens offer several benefits, including:
●
Transparency:
Blockchain’s public ledger ensures all token transactions are transparent and
traceable.
●
Security:
Cryptographic algorithms secure tokens, reducing the risk of fraud and hacking.
●
Accessibility:
Tokens enable global participation in digital ecosystems, transcending
geographical boundaries.
●
Programmability:
Smart contracts allow developers to program specific functionalities into
tokens.
Challenges and Risks
Despite their advantages, tokens come with challenges:
●
Regulatory
Uncertainty: Security tokens, in particular, face complex regulatory
landscapes across different jurisdictions.
●
Volatility:
Cryptocurrency tokens often experience price fluctuations, making them risky
investments.
●
Scalability Issues:
As blockchain networks grow, they may face challenges in handling a high volume
of transactions efficiently.
●
Security
Concerns: While blockchain technology is secure, vulnerabilities can arise
in token smart contracts or wallet storage solutions.
Conclusion
Tokens are an integral part of the digital economy,
with applications spanning finance, gaming, art, and beyond. Understanding
their types and mechanisms is essential for anyone engaging with blockchain
technology. As the industry evolves, tokens will continue to revolutionize how
we interact with digital assets, services, and communities. However, it is
crucial to approach tokens with informed caution, considering their associated
risks and challenges. Whether as an investor, developer, or user, embracing
tokens responsibly can unlock their vast potential in shaping the future.
