HDMI Modulator: A Complete Guide
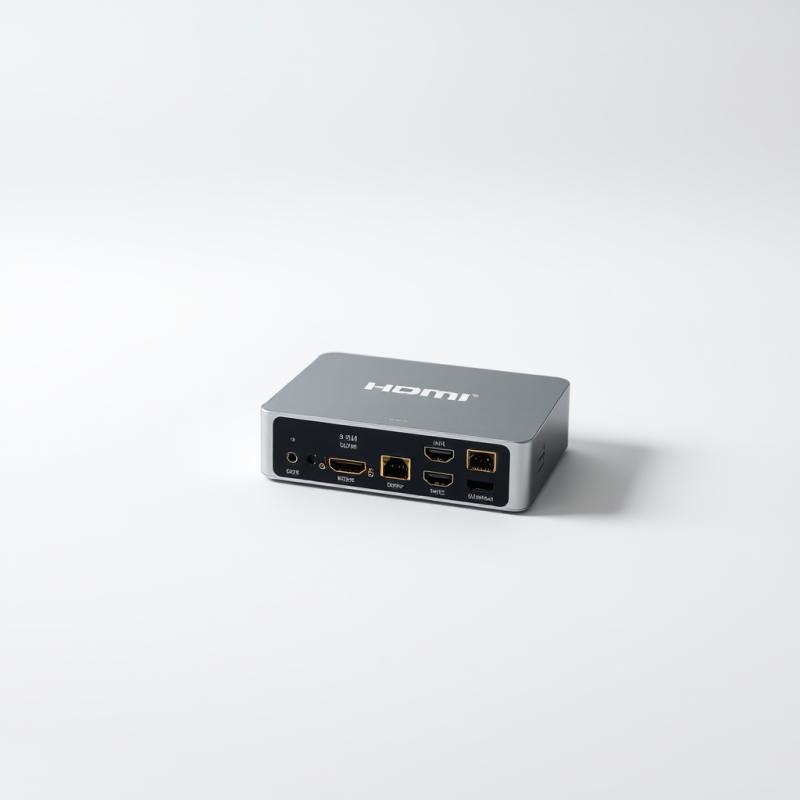

What is an HDMI Modulator?
An HDMI modulator is a specialized device that converts HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) signals into radio frequency (RF) signals, enabling the transmission of high-definition audio and video over coaxial cables. This technology is particularly useful for distributing content to multiple televisions or displays in various settings, such as homes, hotels, and commercial spaces.
A device called an HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) modulator converts an HDMI signal into a modulated radio frequency (RF) signal that traditional TV viewers may receive and broadcast over coextensive cable. This technology enables the distribution and display of high-description videotape and audio signals from HDMI sources (such as Blu-shaft players, computers, game consoles, or streaming bias) to numerous TVs or observers over a radio frequency structure, like a hostel, retail store, or large apartment complex. While RF modulators can work with a variety of signal types and are primarily focused on integrating older analog systems into modern RF networks, HDMI modulators are specialized for handling HDMI signals, guaranteeing high-definition quality. Both types of modulators are used to convert signals for distribution over coaxial cables.
Primary Features of HDMI Modulator
The primary features of an HDMI modulator, particularly an HDMI RF modulator, are essential for ensuring effective signal conversion and distribution. Here are the key aspects:

1. Video Quality and Output Resolution
Most HDMI modulators support high-definition video output, typically at 1080p, with some advanced models offering 4K resolution. This capability is crucial for delivering a high-quality viewing experience, especially in environments where clarity and detail are paramount.
2. Connectivity Options
HDMI modulators come equipped with various input interfaces to connect to different source devices, such as media players, set-top boxes, and gaming consoles. Ensuring compatibility with the necessary input and output formats is vital to avoid connectivity issues.
3. Latency and Synchronization
A good HDMI modulator minimizes latency, ensuring that audio and video remain synchronized during transmission. This feature is particularly important for applications like live broadcasts or video conferencing, where delays can disrupt the viewing experience.
4. Channel Assignment Controls
These modulators allow users to assign specific RF channels to the modulated signal, facilitating seamless integration into existing systems. This feature enables users to tune their TVs to the designated channel for viewing the transmitted content.
5. Signal Amplification
Higher-end models often include built-in amplifiers to boost signal strength, reducing interference and ensuring consistent quality over long distances. This is especially useful in larger installations where the signal must travel through extensive coaxial cable runs.
6. Compact Design
Many HDMI modulators are designed to be small and lightweight, making them easy to install and manage within various settings, from home theaters to commercial environments.
7. User Interface
Some HDMI modulators feature user-friendly interfaces for configuration and adjustments, including physical buttons or digital displays that enhance usability during setup and operation.
In summary, these features collectively enhance the functionality of HDMI modulators, making them versatile tools for distributing high-definition audio and video across multiple screens efficiently.
Key Differences Between HDMI modulators and RF Modulators
The key differences between HDMI modulators and RF modulators lie in their design, functionality, and application. Here’s a detailed comparison:
1. Signal Type and Conversion
HDMI Modulators: Specifically designed to convert HDMI signals (digital) into RF signals. They ensure the preservation of high-definition quality during the conversion process, supporting resolutions up to 4K.
RF Modulators: Generally handle a broader range of signal types, including analog and digital signals. They can convert various input formats into RF signals but may not focus on maintaining high-definition quality as effectively as HDMI modulators.
2. Primary Use Case
HDMI Modulators: Primarily used for distributing high-definition audio and video content from HDMI sources (like Blu-ray players and gaming consoles) over coaxial cables to multiple TVs or displays. They are ideal for modern AV setups that require high-quality video transmission.
RF Modulators: Often used in older systems to integrate analog devices with modern RF networks. They serve to bridge the gap between different technologies, making them suitable for retrofitting existing setups rather than focusing solely on HDMI sources.
3. Quality of Output
HDMI Modulators: Designed to maintain the integrity of the original HDMI signal, minimizing quality loss during modulation. This is critical for applications where video clarity is essential12.
RF Modulators: While they can transmit signals effectively, the quality may vary based on the modulation technique used and the type of input signal being converted. Some RF modulators may experience issues like interference or signal degradation.
4. Compatibility with Systems
HDMI Modulators: Typically require devices with HDMI outputs and are optimized for modern digital TVs that can decode RF signals back into high-definition video.
RF Modulators: More versatile in terms of compatibility, as they can work with both digital and analog systems, allowing integration into older setups that do not support HDMI directly.
5. Channel Management
HDMI Modulators: Often feature advanced channel mapping capabilities, allowing users to assign specific RF channels for different HDMI inputs. This helps in managing multiple streams efficiently within a single installation.
RF Modulators: May also allow channel selection, but their primary focus is on converting various types of signals rather than managing multiple HDMI inputs specifically.
Benefits of Using HDMI Modulator
Using an HDMI modulator offers several significant benefits, particularly for environments that require the distribution of high-definition audio and video across multiple displays. Here are the key advantages:
1. High-Definition Signal Distribution
HDMI modulators enable the transmission of high-definition content (up to 4K) over existing coaxial cable infrastructure. This ensures that viewers receive clear and detailed video quality, which is essential in settings such as homes, hotels, and commercial spaces.
2. Cost-Effectiveness
By leveraging existing coaxial cabling, HDMI modulators eliminate the need for extensive rewiring or installation of new HDMI cables. This makes them a cost-effective solution for large installations where multiple displays need to receive the same content.
3. Long-Distance Transmission
Unlike standard HDMI cables, which can experience signal degradation over long distances, HDMI modulators can transmit signals over coaxial cables without noticeable loss of quality. This is particularly beneficial in larger buildings or facilities where displays are located far from the source.
4. Multi-Device Connectivity
Many HDMI modulators support multiple HDMI inputs, allowing users to connect several devices simultaneously. This flexibility enables the distribution of different content streams to various TVs or monitors, making it ideal for environments like hotels or schools where different users may want to watch different programs.
5. Simplified Installation and Configuration
HDMI modulators are generally easy to install and configure, requiring minimal technical expertise. They can be set up quickly, allowing for efficient integration into existing AV systems.
6. Channel Assignment and Tuning
These devices allow users to assign specific RF channels for each HDMI input, making it easy for viewers to tune their TVs to the correct channel to access the desired content. This feature simplifies content management across multiple screens.
7. Compatibility with Older Systems
HDMI modulators can bridge the gap between modern HDMI devices and older analog systems, enabling users to integrate legacy equipment without needing to replace all their hardware. This is particularly useful for upgrading existing setups while maintaining functionality.
How do HDMI modulators compare to traditional HDMI extenders
HDMI modulators and traditional HDMI extenders serve different purposes in the realm of audio and video signal transmission. Here’s a comparison highlighting their key differences:
1. Functionality
HDMI Modulators: Convert HDMI signals into RF (radio frequency) signals, allowing the distribution of high-definition content over coaxial cables to multiple TVs or displays. They are designed for environments where multiple users need to access the same content from a single source.
HDMI Extenders: Extend the distance of HDMI signals using various methods (like CAT5e/6 cables or wireless technology). They regenerate and transmit the HDMI signal to a remote display, effectively overcoming the short-distance limitation of standard HDMI cables.
2. Signal Quality
HDMI Modulators: Maintain high-definition quality during conversion, supporting resolutions up to 4K. They are optimized for minimal signal degradation when transmitting over coaxial cables.
HDMI Extenders: While they can also support high-definition resolutions, the quality may vary based on the transmission method used (wired or wireless). Wired extenders generally provide a more stable connection with less risk of interference compared to wireless options.
3. Distance Capabilities
HDMI Modulators: Can transmit signals over long distances using coaxial cables without significant quality loss, making them suitable for large installations like hotels or commercial buildings.
HDMI Extenders: The distance depends on the type of extender used. For example, extenders using CAT5e/6 cables can reach up to 100 meters (330 feet), while optical fiber extenders can extend up to 300 meters (1,000 feet) 13. Wireless extenders have varying ranges but may be limited by obstacles and interference.
4. Installation Complexity
HDMI Modulators: Typically require a more complex setup involving RF channel assignment and possibly additional equipment for optimal performance. However, once set up, they can simplify content distribution across multiple displays.
HDMI Extenders: Generally easier to install as they often involve connecting a transmitter and receiver via a single cable (for wired extenders) or setting up wireless components. This makes them user-friendly for extending signals over shorter distances.
5. Use Cases
HDMI Modulators: Best suited for environments where multiple displays need to show the same content from a single source, such as in digital signage, educational institutions, or hospitality settings.
HDMI Extenders: Ideal for scenarios where a single source needs to be connected to a remote display without running long HDMI cables directly. Common applications include home theaters, conference rooms, and situations where devices are located far apart.
6. Cost Considerations
HDMI Modulators: Often more expensive due to their advanced functionality and capabilities in handling multiple channels and high-quality video distribution.
HDMI Extenders: Generally more affordable, especially wired options; however, costs can increase for advanced wireless systems that offer greater flexibility.
FAQs About HDMI modulator
1. What is an HDMI modulator?
An HDMI modulator is a device that converts HDMI signals from sources like Blu-ray players, gaming consoles, or set-top boxes into radio frequency (RF) signals. This allows the signals to be transmitted over coaxial cables to multiple TVs or displays, similar to traditional cable TV systems.
2. How does an HDMI modulator work?
The operation of an HDMI modulator involves three key steps:
Signal Encoding: The device encodes the digital HDMI signal into a format compatible with RF transmission.
Frequency Modulation: The encoded signal is modulated to a specific frequency, allowing it to travel over coaxial cables.
Signal Transmission: The modulated RF signal is sent to connected TVs through coaxial cables, enabling users to tune their TVs to the designated channel.
3. What are the benefits of using an HDMI modulator?
Benefits include:
High-definition video distribution without quality loss.
Cost-effectiveness by utilizing existing coaxial cabling instead of running multiple HDMI cables.
Multi-room AV distribution, allowing content from a single source to be viewed on several TVs.
Long-distance transmission capabilities without significant degradation in quality.
4. Can I use an HDMI modulator with older analog TVs?
Yes, many HDMI modulators are designed to bridge the gap between modern HDMI devices and older analog systems. They can output RF signals that older TVs can receive via coaxial connections.
5. What types of resolutions do HDMI modulators support?
Most modern HDMI modulators support high-definition resolutions up to 1080p, with some advanced models capable of handling 4K resolution.
6. How do I set up an HDMI modulator?
Setting up an HDMI modulator typically involves:
Mounting the device in a suitable location.
Connecting the source device via an HDMI cable.
Attaching a coaxial cable from the modulator's output to the existing coaxial infrastructure.
Powering the unit and configuring settings such as channel assignment.
7. Do I need special equipment to use an HDMI modulator?
While you need a compatible TV or display that can receive RF signals, no additional specialized equipment is necessary beyond standard coaxial cabling and connectors.
8. What is the difference between an HDMI modulator and an HDMI extender?
An HDMI modulator converts HDMI signals into RF for distribution over coaxial cables, suitable for multiple displays. In contrast, an HDMI extender typically extends the distance of an HDMI signal using CAT5e/6 cables or wireless technology, primarily connecting a single source to a remote display.









Comments