How Economic Uncertainty is Shifting Tendering Trends

There is no doubt that the global economy is still on its fragile feet. Businesses have had to bear the burden of economic uncertainty as well as its impacts on everything from day-to-day business activities to long-term strategic work. For businesses seeking government contracts, this uncertainty has changed the tendering landscape and has increasingly complicated the ability of businesses to predict their future with regard to tenders. The global economy itself is shifting and becoming unstable, affecting tender opportunities including government contracts and the changing tides of how businesses keep up to remain in the game. So, here in this Tender Grid blog, we will discuss these things in detail.
Understanding Tendering and Government Contracts
Tendering refers to the process by which companies submit their bids to win contracts, mainly government contracts. It is thus crucial since most government procurement comes with a hefty contract value and a long tenure, providing a secure source of income for businesses. These government tenders range from construction and technology to health care, infrastructure, and many more.
Government contract tendering was often well organized and long-term prior to economic uncertainty beginning to creep up. The governments would set budgets for projects, and companies generally were pretty sure what to expect within a relatively stable timeline, and governments would set budgets for projects. However, as the global economy faces challenges—ranging from inflation to supply chain disruptions government procurement practices are evolving in response.
The Impact of Economic Uncertainty on Tendering
Global Economic Shifts
The last two or three years have noticed global economic shocks that have continued up to this day—from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic to ongoing energy crises and inflationary pressures. These factors really add an aspect of uncertainty in itself that impacts how businesses plan, budget, or compete for contracts. Consequently, governments are seen to change their procurement strategies based on the same reasons.
For instance, inflation has made several governments tighten up their budgets. It has cut down funds for certain projects and compelled others to scale down the scope and scale. This has made the game of tendering more aggressive and less predictable.
Government Budgets and Expenditure
Fiscal tightening is usually related to economic instability, which the government has to engage in to cut or delay spending on certain sectors. Shrinking budgets may put infrastructure or defence projects on hold or scaled back, while additional funds may be supplied for health services or disaster relief.
This shift in spending priorities leads to direct impacts in terms of tender opportunities. Governments may place more emphasis on cost-effectiveness and short-term solutions, adjusting their criteria for awarding contracts. The opportunity for global tenders may then lean more toward short-term objectives rather than long-term ones.
Risk Aversion and Short-Term Contracts
Since the operations requirements cannot be completely eradicated, companies as well as governments become more careful at times of uncertainty. Governments get more nervous when their chances of budget overruns or surprise expenses inflate. Short-term contracts are sometimes resorted to with the flexibility to switch tracks much faster. Moreover, smaller-scope contracts help mitigate the risks associated with mega projects; such big-ticket projects might well have become too financially unfeasible.
For businesses, the shift to short-term contracts can present both challenges and opportunities. While these projects may offer less financial stability in the long run, they can provide a quicker return on investment and offer a pathway to future contracts if managed well.
Key Shifts in Tendering Trends
As economic uncertainty impacts government procurement, there are several key changes in how government tenders are structured and awarded. The following table summarizes these shifts, providing a quick overview of what businesses can expect when bidding for government or global tenders.
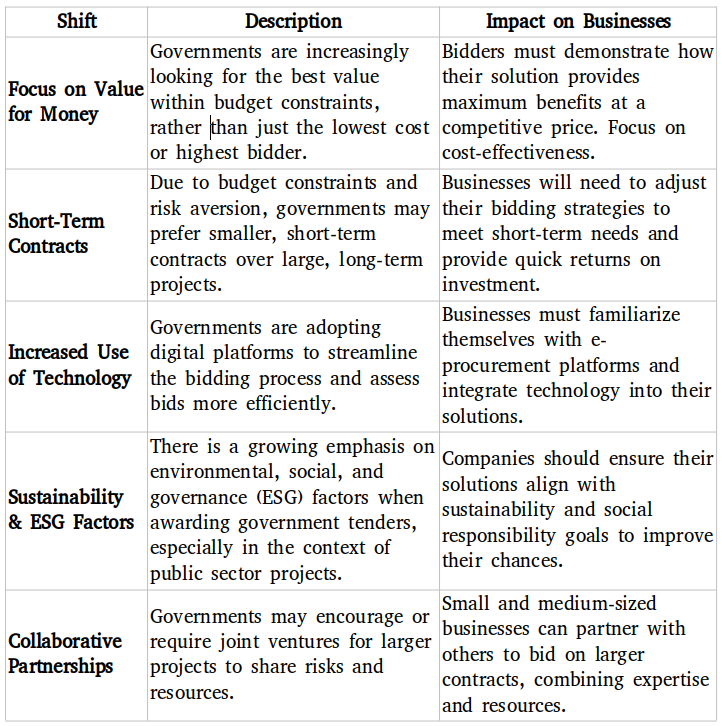
Navigating Tendering Opportunities in a Shifting Landscape
Illustration of Successful Adaptation
Challenges for Suppliers and Bidders
Increased Competition
Complex Tender Documents and Regulations
Delayed Payments and Cash Flow Issues
Future Outlook: What to Expect in the Coming Years
Conclusion
Post Your Ad Here


Comments