Types of Fibroids: What Every Woman Should Know
Uterine fibroids, benign tumors that grow in the uterus, affect
many women worldwide. They come in various types, each with distinct
characteristics and implications for women's health. In this article, we delve
into the different types
of fibroids, their locations, symptoms, and potential treatment options.
Intramural Fibroids: The Most Common Type
Intramural fibroids are the most prevalent type, growing within
the muscular wall of the uterus. These fibroids can vary in size and often
cause pressure symptoms, such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pain during
intercourse, and pelvic discomfort. They can also lead to changes in the shape
of the uterus, which may complicate pregnancy or cause fertility issues. Women
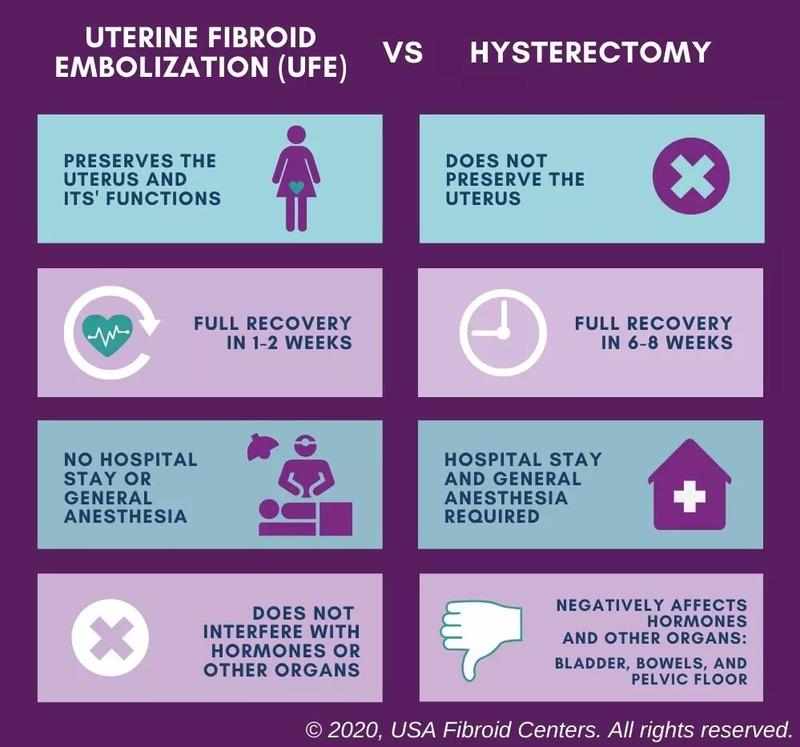
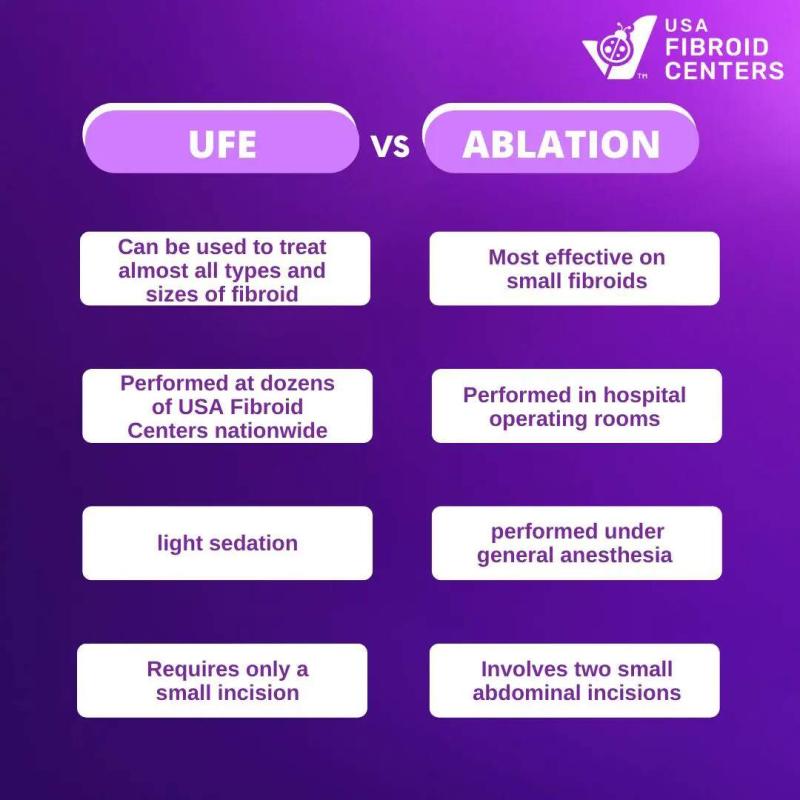
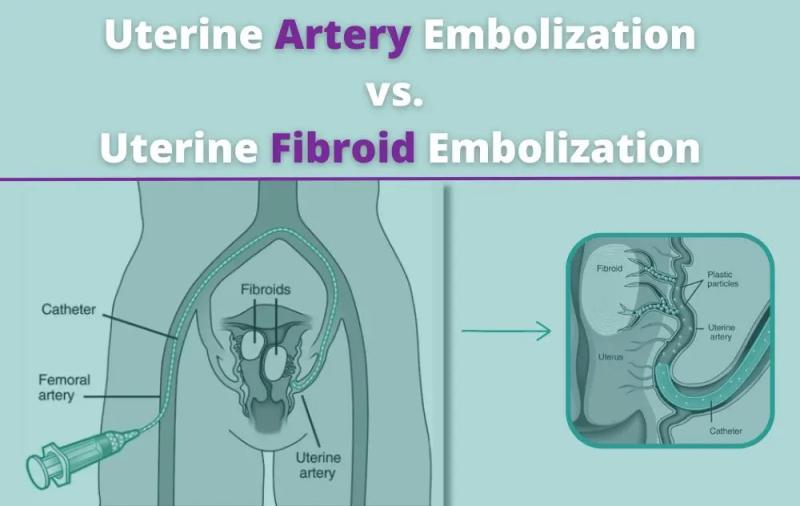
with intramural fibroids often seek treatment options like Uterine Fibroid
Embolization (UFE) or myomectomy to alleviate symptoms.
Subserosal Fibroids: External Growths
Subserosal fibroids grow on the outer surface of the uterus. These
fibroids can become quite large, leading to pressure on surrounding organs,
such as the bladder and rectum. Women with subserosal fibroids may experience
back pain, frequent urination, or constipation. Their location often makes them
easier to remove surgically, but they can still cause significant discomfort.
Understanding the symptoms associated with subserosal fibroids can help women
make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Pedunculated Fibroids: Stalked Growths
Pedunculated fibroids are unique in that they are attached to the
uterus by a stalk or peduncle. They can develop either subserosally or intramurally.
If a pedunculated fibroid twists, it can cause acute pain, requiring immediate
medical attention. These fibroids may also lead to complications during
pregnancy if they obstruct the birth canal. Understanding the characteristics
of pedunculated fibroids is crucial for early intervention and management.
Submucosal Fibroids: Inside the Uterine Lining
Submucosal fibroids develop just beneath the uterine lining,
potentially protruding into the uterine cavity. These fibroids can
significantly impact menstrual cycles, often causing heavy bleeding and
prolonged periods. Women with submucosal fibroids may experience fertility
challenges, as these fibroids can interfere with embryo implantation. Treatment
options may include hysteroscopic surgery, which allows for the removal of
fibroids through the cervix, preserving the uterus.
Calcified Fibroids: Changes Over Time
Calcified fibroids occur when fibroids undergo a process of
calcification, often due to aging or lack of blood supply. While these fibroids
are typically not harmful, they can cause discomfort and other symptoms similar
to other fibroid types. Regular monitoring through ultrasound can help assess
the size and impact of calcified fibroids on a woman’s health. Understanding
the implications of calcified fibroids is essential for women facing this
condition.
Fibroids with Associated Symptoms: Recognizing the Signs
Each type of fibroid can present a variety of symptoms that can
vary from woman to woman. Common symptoms include heavy menstrual bleeding,
pelvic pain, and pressure symptoms. Recognizing these signs can lead to earlier
diagnosis and intervention. It's essential for women to consult healthcare
professionals if they suspect they have fibroids, as timely treatment can
significantly improve their quality of life.
Size Matters: The Impact of Fibroid Size on Symptoms
The size of fibroids plays a significant role in determining the
severity of symptoms. Smaller fibroids may go unnoticed, while larger ones can
cause considerable discomfort. Treatment options vary depending on the size and
type of fibroid, with options ranging from medication to surgical
interventions. Women should have open discussions with their healthcare
providers about the implications of fibroid size on their health and treatment
plans.
Risk Factors for Developing Fibroids: What to Know
Several risk factors can contribute to the development of
fibroids, including genetics, age, and hormonal influences. Understanding these
factors can empower women to take charge of their health. For instance, women
with a family history of fibroids are at a higher risk. Awareness of risk
factors can lead to proactive measures, such as regular check-ups and
screenings, to monitor for fibroid development.
Diagnosis of Fibroids: How Are They Identified?
Diagnosing fibroids typically involves a combination of medical
history, physical examinations, and imaging tests like ultrasound or MRI. These
tests help identify the type, size, and location of fibroids. Women
experiencing symptoms related to fibroids should consult their healthcare providers
for accurate diagnosis and to discuss appropriate treatment options based on
their specific situations.
Treatment Options for Different Types of Fibroids: Making Informed
Choices
Treatment for fibroids varies based on the type, size, and
severity of symptoms. Options include watchful waiting, medication, UFE, and
surgical procedures like myomectomy or hysterectomy. It’s crucial for women to
understand the pros and cons of each treatment option to make informed
decisions that align with their health goals and lifestyle. Consulting with a
fibroid specialist can provide valuable insights into the best course of
action.





Comments