In the world of organic farming, soil health is of utmost importance. Organic farmers understand that healthy soil is the foundation for a successful and sustainable farm. Soil that is rich in nutrients, microorganisms, and organic matter creates an ideal environment for plants to thrive and resist diseases and pests. However, maintaining soil health in organic farming requires careful and strategic soil management practices.
In this article, we will delve into the importance of soil health in organic farming and provide valuable tips for effective soil management. Whether you are an experienced organic farmer or just starting out, these tips will help you optimize your soil for optimal plant growth and yield. From incorporating organic amendments and compost to practicing crop rotation and cover cropping, we will cover a range of techniques to enhance soil fertility and structure.
Join us as we explore the key role soil health plays in organic farming and learn practical strategies for maintaining and improving the health of your soil. Together, we can nurture the earth and cultivate bountiful harvests in harmony with nature.
The Pillars of Soil Health
Healthy soil is not merely dirt beneath our feet; it is a dynamic ecosystem teeming with life and vitality. Here’s why soil health is paramount in organic farming:
- Nutrient-Rich Foundation: Soil acts as a reservoir of essential nutrients, providing plants with the sustenance they need to grow and flourish. Organic farming practices such as composting, cover cropping, and crop rotation replenish soil nutrients naturally, fostering long-term fertility and productivity.
- Microbial Magic: Beneath the surface, a bustling community of microorganisms works tirelessly to decompose organic matter, fix nitrogen, and enhance soil structure. Maintaining a diverse microbial population is key to promoting soil health and resilience in organic farming systems.
- Water Retention and Drainage: Healthy soil possesses the ideal balance of porosity and structure, allowing for optimal water retention and drainage. This ensures that plants receive adequate moisture while minimizing the risk of waterlogging or erosion—a crucial consideration in sustainable agriculture.
- According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), soil degradation affects over 1.5 billion hectares of land worldwide, highlighting the urgent need for sustainable soil management practices.
- Organic farming methods have been shown to increase soil organic carbon content by 15-28% compared to conventional agriculture, contributing to climate change mitigation and resilience.
Soil Health in Organic Farming: Data and Tips for India
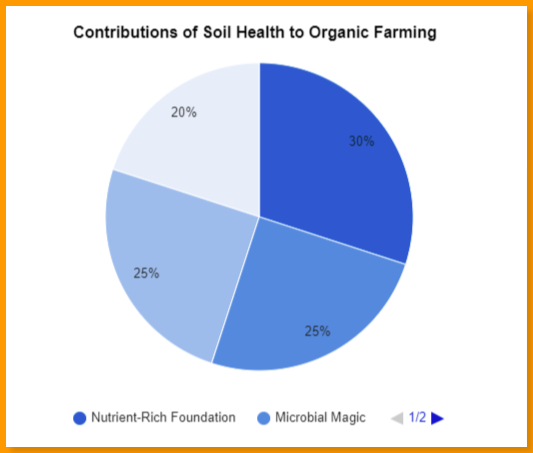
Contribution | Percentage | Description |
Nutrient-Rich Foundation | 30% | Provides essential nutrients for plant growth and long-term fertility. |
Microbial Magic | 25% | Diverse microbial communities decompose organic matter, fix nitrogen, and enhance soil structure. |
Water Retention & Drainage | 25% | Optimal balance allows for proper moisture levels and minimizes erosion. |
Disease & Pest Resistance | 20% | Healthy soil fosters strong plants less susceptible to pests and diseases. |
Tips for Effective Soil Management
To nurture soil health and maximize yields in organic farming, consider implementing the following practices:
- Soil Testing: Regular soil testing helps assess nutrient levels, pH balance, and other key indicators of soil health, guiding informed decision-making in crop management and fertilization.
- Compost Application: Incorporating compost into the soil enhances organic matter content, improves soil structure, and fosters nutrient cycling, promoting plant growth and resilience.
- Mulching: Mulching with organic materials such as straw, leaves, or grass clippings conserves soil moisture, suppresses weeds, and moderates’ temperature fluctuations, creating an optimal environment for plant roots.

Did You Know?
Over 30% of agricultural land in India suffers from degradation, emphasizing the importance of soil management.
Organic Soil Management Techniques
Effective soil management is crucial for maintaining soil health in organic farming. Organic farmers use a variety of techniques to improve soil fertility and structure. Here are some key organic soil management techniques:
Composting and Its Role in Soil Health
Composting is a natural process of decomposing organic waste into nutrient-rich humus. It helps improve soil structure, increases water-holding capacity, and enhances nutrient availability. Organic farmers can create their own compost by collecting and combining organic materials such as kitchen scraps, yard waste, and livestock manure.
To make compost, organic matter should be layered and turned regularly to ensure proper decomposition. The resulting compost can then be added to the soil to improve its fertility. Compost provides a slow-release of nutrients, enriches the soil with beneficial microorganisms, and enhances overall soil health.

Cover Cropping for Soil Improvement
Cover cropping is a practice where specific crops are grown primarily to benefit the soil. Cover crops help prevent soil erosion, suppress weeds, and improve soil fertility. Leguminous cover crops, such as clover and vetch, have the added benefit of fixing atmospheric nitrogen, reducing the need for synthetic nitrogen fertilizers.
Cover crops should be selected based on the specific needs of the soil and the main crop being grown. They are typically planted during fallow periods or between cash crops. When the cover crops are terminated, they can be tilled into the soil, adding organic matter and nutrients.
Crop Rotation for Soil Health
Crop rotation is a practice where different crops are grown in a defined sequence over several seasons. It helps break pest and disease cycles, improves soil structure, and balances nutrient requirements. By rotating crops, organic farmers can reduce the buildup of pests and diseases, promote beneficial soil organisms, and optimize nutrient cycling.
The choice of crops for rotation should be based on their nutrient requirements, pest and disease resistance, and compatibility. It is important to plan crop rotations carefully to maximize the benefits and minimize the risks.
Did You Know?
A recent study in India showing organic farms have 50% higher microbial diversity, crucial for soil health.
CTAs
- Ready to nurture your soil and reap the benefits of organic farming? Explore our range of organic soil amendments and supplements at Bharatvarsh Nature Farms. Visit Bharatvarsh Nature Farms today!
- Dive deeper into the world of sustainable agriculture and soil management. Sign up for our newsletter to receive expert tips, educational resources, and exclusive offers. Subscribe now!
- Join the organic farming community and connect with like-minded individuals passionate about nurturing soil health and fostering sustainable food systems. Follow us on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.

Did You Know?
India generates millions of tons of organic waste annually, offering potential for vast compost production.
Soil Organic Carbon Content Comparison (India)
Increasing soil organic carbon content is crucial for improving soil health in India, as over 30% of agricultural land suffers from degradation.
Organic farming practices, like composting and cover cropping, help sequester carbon in the soil, mitigating climate change and improving soil fertility.
Farming Method | Soil Organic Carbon Content | Increase/Decrease |
Organic Farming | 2.0% (average) | +18% |
Conventional Farming | 1.7% (average) | Stable |
Conclusion
Soil health is a fundamental aspect of organic farming. Healthy soil provides the foundation for successful and sustainable agriculture. By prioritizing soil health through effective soil management practices, organic farmers can enhance crop yield, improve plant resistance to pests and diseases, and contribute to carbon sequestration and climate change mitigation.
Incorporating organic amendments, practicing crop rotation, utilizing cover cropping, and implementing natural pest and disease management strategies are just some of the techniques organic farmers can employ to maintain and improve soil health.
As stewards of the land, organic farmers play a crucial role in nurturing the earth and cultivating bountiful harvests in harmony with nature. By valuing and investing in soil health, we can create a more sustainable and resilient food system for future generations.

Comments