The Essential Role of Manual Check Valves in Industrial Valve Applications
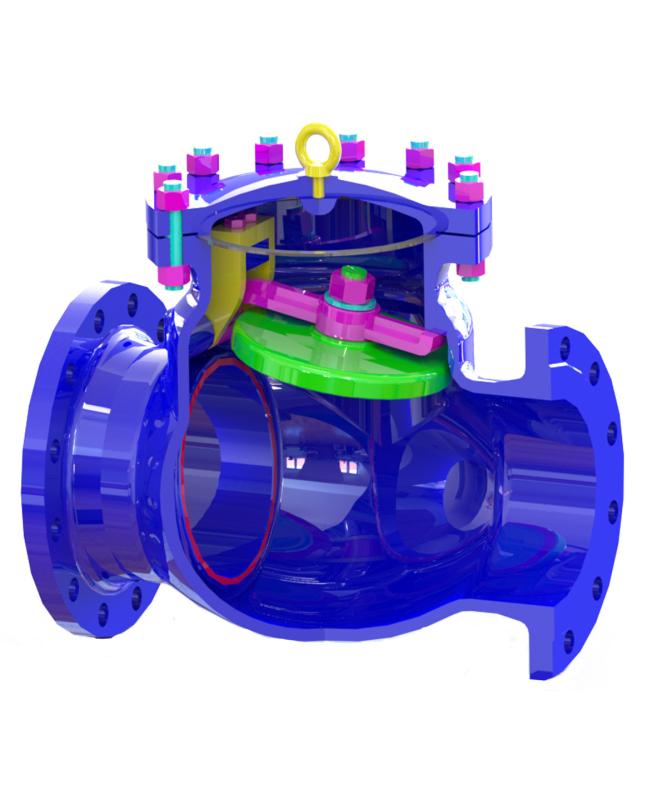

In this article, we'll explore the essential aspects of manual check valves and industrial valves, discussing their functions, applications, types, and benefits in the industrial setting.
One of the significant challenges with varying processes within an industrial context is flow and pressure regulation in the manufacturing process. Valves are essential in controlling the flow of a system's liquid, gas, and slurry while ensuring safety and productivity standards. The role of manual check valves has become especially crucial in studying the numerous classifications of valves. These valves are an affordable but very effective means for preventing backflow of fluids in industrial applications.
What is a Manual Check Valve?
A Manual Check Valve helps the fluid's one-way flow and restricts the fluid's backward flow. Manual check valves are entirely different from automated ones, which function automatically. A manual check valve moves manually by the user and allows the user to open or close whenever the user wants to. These valves are generally developed to be easy to build and utilize, delivering dependability and durability in different industrial applications.
Prior Function: To control backflow in a pipeline.
Manual Operation: Manually operated so that personnel can decide when the valve needs to be opened or closed.
It can prevent the undesired backflow, avoid pressure accumulation, and maintain its efficiency in industrial systems.
Key Features of Manual Check Valves
Regarding industrial applications, the specific features of manual check valves make them indispensable in certain situations. Key features include:
One-Way Flow Control: Designed to allow fluid to flow in one direction only, ensuring system integrity by preventing backflow.
Simple Construction: Fewer moving parts make them easy to maintain and operate.
Manual Override: Unlike automated systems, manual check valves give operators control over flow management.
Pressure Sensitive: These valves react to differential pressure; they open when forward pressure is applied and close when reverse pressure is detected.
Applications of Manual Check Valves in the Industry
Manual check valves are widely used across many industries due to their simplicity, effectiveness, and reliability. Some of the most common applications include:
Water and Wastewater Treatment Plants: These valves help regulate water flow and prevent backflow contamination in treatment processes.
Oil and Gas Industry: Used to prevent reverse flow in pipelines and ensure the smooth transport of oil, gas, or other petrochemical substances.
Chemical Processing: Employed to ensure that hazardous chemicals are safely controlled and do not flow backward into critical systems.
HVAC Systems: Prevents the backflow of refrigerants or air, helping to maintain system efficiency and prevent contamination.
Power Generation Plants: These are used in cooling systems to prevent reverse water flow that could damage turbines or other critical equipment.
Types of Manual Check Valves
Manual check valves come in various types to accommodate different industrial needs. The type of valve selected depends on the controlled fluid, environment, and system requirements.
Swing Check Valves
The most common check valve type features a hinged disc that swings open or closed depending on the flow direction.
Well-suited for large pipelines, such as in water and wastewater industries.
Works efficiently in low-pressure systems.
Lift Check Valves
These valves lift open when forward pressure is applied and drop down to block reverse flow.
Best used in high-pressure applications.
Common in steam systems and gas pipelines.
Ball Check Valves
Utilizes a spherical ball to block the flow, which lifts when fluid moves in the correct direction.
Compact design, often used in small pipelines.
Ideal for handling slurries or fluids with particulates.
Tilting Disc Check Valves
Designed for smooth and efficient flow control with a disc that tilts to open and close.
Allows for higher flow rates with minimal energy loss.
Typically used in large-scale applications like power plants.
Key Industrial Valve Categories
Beyond manual check valves, the world of industrial valves is vast, with numerous types of valves that serve specific purposes in industrial systems. Some of the critical Industrial Valve categories include:
Gate Valves
Primarily utilized to start or stop the flow of liquid.
Best for applications where the flow needs to be controlled fully or stopped altogether.
Used in industries like oil and gas, water treatment, and manufacturing.
Globe Valves
Designed for throttling or regulating fluid flow.
Ideal for systems where precise flow control is required.
Commonly found in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and power generation sectors.
Ball Valves
Features a ball with a hole in the center that allows or blocks flow.
Offers fast operation and is well-suited for high-pressure applications.
Utilized in industries ranging from food processing to oil and gas.
Butterfly Valves
Lightweight and designed for quick shut-off of fluid flow.
Suitable for large-diameter pipes and often used in water distribution systems.
Known for their energy-efficient performance.
Pressure Relief Valves
Designed to release excess pressure from a system to avoid damage or failure.
Critical for ensuring safety in high-pressure applications like boilers or gas pipelines.
Diaphragm Valves
Utilizes a flexible diaphragm to control flow.
Ideal for corrosive or viscous fluids.
Often found in the chemical processing and pharmaceutical industries.
Final Words
Choosing the correct valve and Ball Valve Seat Materials is critical to ensuring system efficiency, longevity, and safety. Understanding valves' various types and applications helps make informed decisions when designing and maintaining industrial systems.








Comments