Various Components of The Engine Management System Of A Vehicle
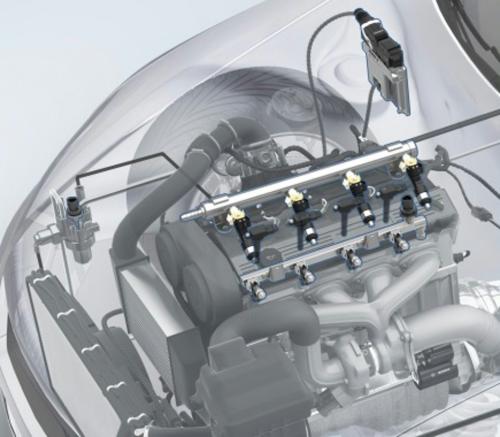
The Engine Management System of a vehicle controls the amount of fuel injected to the engine and adjusts the timing of ignition. Proper functioning of an Engine Management System ensures minimum exhausts emission, lowest consumption of fuel and more engine power. The Engine Management System is primarily a custom made computer that monitors the speed, temperature and load of the engine. It can be divided into two different subsystems, fuel system and ignition system. Besides knowing about the existence of these two systems, it is also essential to have an idea about the various other components of the Engine Management System.
Electronic Control Unit (ECU) – It is the computer part of the Engine Management System that translates the information generated by different sensors and measures the exact ratio of the air/fuel mixture at any given circumstance. After that, it stimulates the injectors to inject fuel and beckons the distributor for producing a spark.
Fuel Injectors – Fuel injectors are electro-mechanical equipments and their main purpose is to inject the fuel inside the induction component, in the form of a misty spray. The ECU transmits an electric vibration to the injector which energises it to release the fuel.
Air Flow Metre – It calculates the amount of air which is drawn inside the engine and signals the ECU to regulate the quantity of fuel required for the provision of the correct fuel/air mixture.
Engine Temperature Sensor – Helps the ECU to sense the exact temperature of the engine which then determines the fuel amount needed by the engine.
Air Temperature Sensor – This component helps the ECU to detect variations in the temperature of the air by transmitting a signal to it. It is situated inside the inlet ducting or in the Air Flow Metre.
Electric Fuel Pump – It is situated inside the tank of fuel or on fuel line and maintains a constant fuel flow to injectors under a fixed pressure.
Fuel Filter – It is usually placed within the fuel line, in the middle of the electric fuel pump and the fuel injectors. A fuel filter is in the shape of a metal can that is fitted inside with a substance made of paper.
Fuel Pressure Regulator - A fuel pressure regulator maintains a constant pressure in the fuel line.
Auxiliary Air Valve – When the engine is idle at a greater speed during a load on the electrical system or at the time of warm up, the auxiliary air valves act as the throttle by-pass.
Throttle Position Switch – Indicates the status of throttle flap.
Crank Angle Sensor – Provides information about the speed of the engine and position reference of the foremost piston for timing of injection.
Institutes for Automotive training courses in Ireland provide general information about these parts and also teach the different methods to detect faults and problems in the fundamental components of the Engine Management System. So, if you want to know more about these components, there are practical courses for you to undertake.

Comments