From Fibroids to Ovarian Cysts: A Guide to Benign Gynecological Tumors
As women, we are no strangers to
dealing with various health issues, including those related to our reproductive
system. One common problem that many women face is benign gynecological tumors,
such as fibroids and ovarian cysts. These conditions can cause discomfort and
even impact fertility, making it important to understand and seek proper
treatment. As a gynecologist in Indore, I have encountered many
patients with these tumors and understand the need for awareness and education
around them.
Firstly, let's understand what
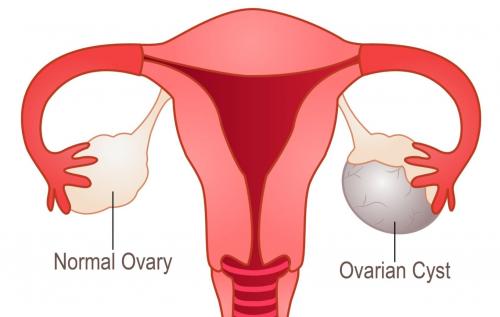
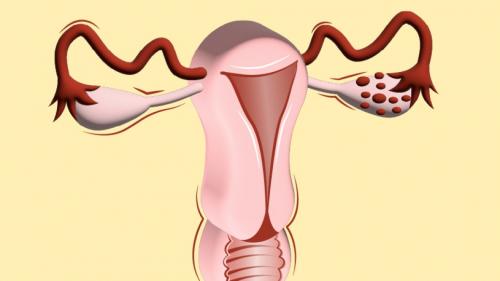
exactly are fibroids and ovarian cysts. Fibroids are non-cancerous growths that
develop in the uterus, while ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form on
the ovaries. Both of these conditions are quite common, with fibroids affecting
about 20-80% of women and ovarian cysts being found in almost all premenopausal
women at some point in their lives.
The symptoms of fibroids and ovarian
cysts can vary from person to person. Fibroids can cause heavy and prolonged
menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and pressure on the bladder or rectum. On the
other hand, ovarian cysts can cause pain in the lower abdomen, bloating, and
changes in menstrual cycles. In some cases, these tumors may not cause any
symptoms and are only discovered during routine gynecological exams.
Also Read: Best Gynaecologist in Indore
While the exact cause of these tumors
is still unknown, certain factors can increase the risk of developing them.
These include hormonal imbalances, family history, and obesity. It is essential
to note that these tumors are not cancerous and do not increase the risk of
developing ovarian or uterine cancer.
Now, let's talk about the diagnosis
and treatment of fibroids and ovarian cysts. Gynecologists in Indore use various methods to diagnose
these tumors, including pelvic exams, ultrasounds, and blood tests. In some
cases, a biopsy may be required to rule out any cancerous growth. The treatment
options for these tumors depend on the size, location, and severity of
symptoms.
For fibroids, the treatment options
include medication to regulate hormones and reduce symptoms, minimally invasive
procedures to remove the fibroids, or surgery to remove the entire uterus
(hysterectomy) in severe cases. Ovarian cysts, on the other hand, may resolve
on their own, or medication may be prescribed to shrink them. In some cases,
surgery may be required to remove the cysts or the entire ovary.







Comments